Fig. 1.
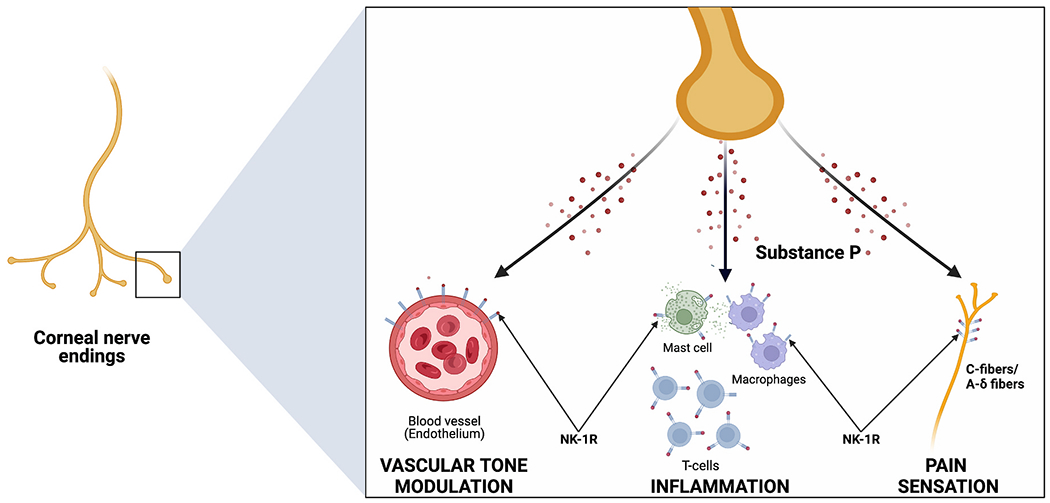
Substance P is primarily released by the corneal nerve endings and acts primarily via the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R). (1) It causes vasodilation and increased permeability of the microvasculature directly, and indirectly through degranulation of mast cells. (2) It has pro-inflammatory effects through activation of T-lymphocytes and macrophages. (3) SP also plays in essential role in pain transmission to the CNS via Aδ and C fibers.
