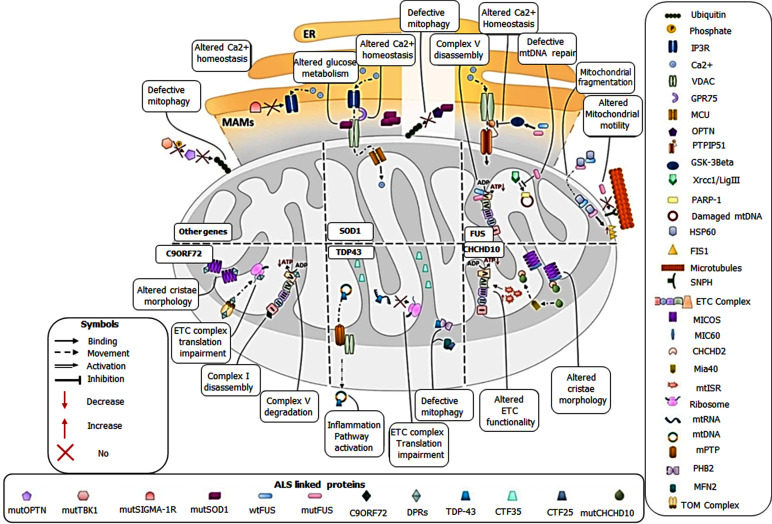
Fig. (2).
Graphical representation of consequences of mitochondrial dysfunction in ALS. Figure shows culprit genes of ALS and their associated pathways causing mitochondrial dysfunction. Other genes (tbk1, optn, sigma-1R) affect calcium homeostasis and mitophagy. SOD1 affects glucose metabolism, calcium homeostasis and mitophagy. FUS affects complex V assembly, mtDNA repair, mitochondrial motility/fragmentation, and calcium homeostasis. CHCHD10 affects cristae morphology and ETC function. TDP43 affects mitophagy, ETC complex translation and inflammation pathway. C9orf72 affects cristae morphology, ETC complex translation, complex I assembly and complex V degradation. Reproduced from ‘Metabolites’, Volume 12, authored by Niccolo Candelise, et al. Mechanistic Insights of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: An Update on a Lasting Relationship. Copyright © 2022 by the authors. Published by MDPI.; open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).