Table 1.
Mitochondria based therapeutic interventions of ALS along with their molecular mechanism and disease conditions.
| S. No. | Interventions | Structure | Mechanism | Disease Condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Exercise or Aerobic endurance |

|
Mitochondrial biogenesis and increased muscle mitochondrial enzyme activities and muscle strength | ALS: Mitochondrial Diseases like Mitochondrial myopathy in ALS and other indications | [119-123] |
| 2 | Riluzole |
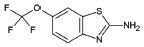
|
Diminishes the ROS generation via anti-glutamatergic effects tendency and attenuates inward calcium current | ALS: Maintaining mitochondrial calcium buffering mechanisms in ALS | [112, 113] |
| 3 | Edaravone |
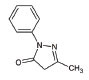
|
Neuro-protective effect by boosting prostacyclin production, reducing lipoxygenase metabolism of arachidonic acid by blocking hydroxyl radicals, preventing alloxan-induced lipid peroxidation and quenching active oxygen species | ALS: Free radical scavenger and antioxidant in ALS | [115] |
| 4 | Fenofibrate |
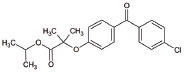
|
PPAR-α activation | ALS: Neuroinflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in ALS | [124] |
| 5 | Vitamins C (Ascorbic Acid) |
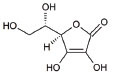
|
Endogenous defensive strategy against oxygen free radicals in mitochondria Protection against lipoperoxidation | ALS: Electron carrier and Antioxidant in ALS |
[125] |
| 6 | Vitamin E (α-tocopherol) |
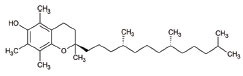
|
Protection against lipoperoxidation | ALS: Lipophilic antioxidant has the ability to cross cell membrane resulting in delay and lower risk of clinical onset in ALS Decrease in plasma levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive species |
[126, 127] |
| 7 | Co-enzyme Q10 (CoQ10) |
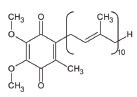
|
A strong lipid oxidants scavenger, which participates in transferring electrons from mitochondrial complexes I and II to mitochondrial complex III. CoQ10: stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential, prevents cytochrome c release; inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition pore, and blocks. Bax translocation to mitochondria |
ALS: Stabilized the motor neuron function in neuro-degenerative disorders like ALS and other indications | [128-131] |
| 8 | Glutathione (GSH) |
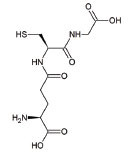
|
Antioxidant property: Neuronal GSH helps in the protection of neurons in the brain against ROS and oxidative damage |
ALS: Regulates the development and progression of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | [132] |
| 9 | Resveratrol |
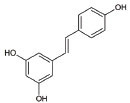
|
Inhibits mutant SOD1 (G93A) protein, up-regulates SIRT1, down-regulates AMPK/SIRT1 signalling and activates mitochondrial biogenesis | ALS: Improves muscle atrophy and mitochondrial dysfunction in ALS and other indications | [133-135] |
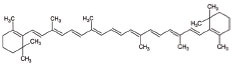
| 10 | β-carotene |
|
Antioxidant properties | ALS: Neuroinflammation and apoptosis in ALS. | [136] |
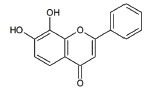
| 11 | 7,8-Dihydroxy-flavone (7,8-DHF) |
|
Modulates metabolic pathways and Improves motor deficits and enhances lower neuronal survival | ALS: Chronic administration of 7,8-DHF improved motor deficits in ALS | [137] |
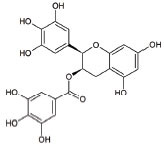
| 12 | Epigallocatechin Gallate |
|
Protection against Lipoperoxidation, diminishes the level of NF-kB, caspase-3 and iNOS |
ALS: Delays the advancement of ALS by alterations in intracellular signals, enhances survival signals (like PI3-K and Akt) and lowers death signals (like GKS-3ß, cytosolic cytochrome c, activated caspase3 and cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase) in ALS and other indications | [138-140] |
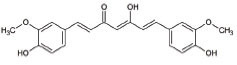
| 13 | Curcumin |
|
Activates Nrf2, reduces intra-cellular ROS levels, and eradicates excitability induced by TDP-43 | ALS: Decreases ALS progression by reducing oxidative damage and improves survival, especially in bulbar onset patients | [140, 141] |
| 14 | Melatonin |
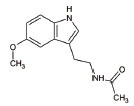
|
Antioxidant effect regulates mitochondrial dysfunction and bioenergetic function | ALS: Orally high doses delayed ALS progression via caspase-1/cytochrome c/caspase-3 cell death pathway, inhibits MT1 receptor loss and increases the survival rate | [141-143] |
| 15 | SBT-272 | NA | Novel peptidomimetic, a role in mitochondrial energetics, by increasing ATP production and decreasing levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in dysfunctional mitochondria | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | Stealth BioTherapeutics |
| 16 | MitoQ | - | Accumulates within mitochondria and protects it from oxidative damage | ALS: slowed the mitochondrial functional decline in the spinal cord and muscle; decreased nitroxidative damage in the nervous system; increased survival and slowed the progression of ALS symptoms. | [144] |
| 17 | Albrioza | - | Reduces neuronal death by blocking key cellular death pathways of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum |
ALS: neuronal protection | [116-118] |
