Table 2.
Mitochondria targeted agents (small molecules) in other than ALS indications.
| S. No. | Interventions | Structure | Mechanism | Disease Condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
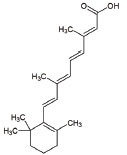
| 1 | All-trans retinoic acid (ARTA/Retinoic acid) |
|
Retinoic acid used for Mitochondria biogenesis and stimulated the retinoid X receptor-α (RXRα) to repair the mitochondrial respiratory chain defect | Lipid metabolism | [119, 148] |
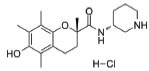
| 2 | KH176 |
|
Intracellular reduction-oxidation-modulating compound used for the management of mitochondrial diseases | MELAS, LHON, Leigh, and other MDs | NCT02544217 & [149] |
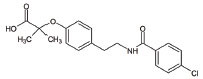
| 3 | Bezafibrate |
|
Mitochondrial biogenesis and PPAR-α activation | Mitochondrial myopathy | [150] |
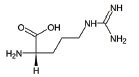
| 4 | L-Arginine |
|
Improvement in aerobic capacity and muscle metabolism | Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like syndrome (MELAS) | NCT01603446 & [151] |
| 5 | Rapamycin |
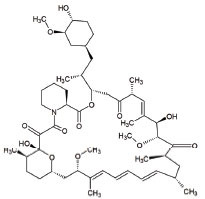
|
Improves motor endurance, muscle morphology, activation of autophagy via mTOR-dependent pathways and mitochondrial structure | Mitochondrial myopathy | [119, 152] |
| 6 | Vatiquinone or EPI-743 |
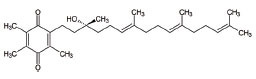
|
EPI-743 works by enhancing the regulation of cellular energy metabolism by directing NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) | Leigh Syndrome and congenital respiratory chain diseases | [153] |
| 7 | Idebenone |
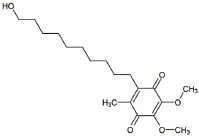
|
Idebenone stimulated the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) | Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) |
[154] |
| 8 | Cysteamine bitartrate |
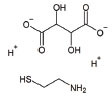
|
Antioxidant properties by enhancing glutathione biosynthesis | Mitochondrial respiratory chain disease | [155] |
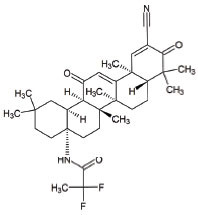
| 9 | Omaveloxolone |
|
Omaveloxolone is an Nrf2-inducer, reduces Inflammation, provides protective shelter to mitochondrial depolarization, promoting mitochondrial respiration and preventing cell death | Friedreich’s Ataxia (FRDA): an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder | [156] |
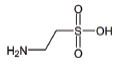
| 10 | Taurine |
|
Neuroprotector by decreasing ER stress and antagonizing neurotransmitter receptors of GABAA, glycine and NMDA | Myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) | [157, 158] |
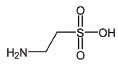
| 11 | L-Carnitine |
|
L-carnitine translocate the fatty acids into the mitochondrial compartment for β-oxidation. Role in carbohydrate metabolism like ketogenesis and glucogenesis. Elimination of toxic metabolites |
Mitochondrial dysfunction, Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) |
[159, 160] |
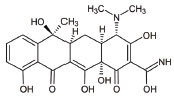
| 12 | Tetracycline |
|
Antiapoptotic, antiinflammation, antioxidation and improves fitness | Mitochondrial dysfunction and Leigh syndrome | [160, 161] |
| 13 | Doxycycline |
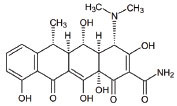
|
Prevents neuronal death and the accumulation of neuroimmune and inflammatory proteins | Mitochondrial dysfunction | [161] |
| 14 | Pioglitazone |
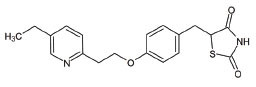
|
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) agonist | Pioglitazone improves lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioural loss, inflammation, white matter injury and mitochondrial dysfunction, inhibits diabetes-induced atrial mitochondrial oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics |
[162, 163] |
| 15 | Sonlicromanol |
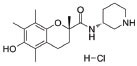
|
Improves neuronal network dysfunction | Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) | [164] |
| 16 | Oleanolic acid |
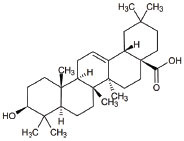
|
Rescued mitochondrial ultra-structure anomalies and mitochondrial biogenesis | Cardiac aging | [165] |
