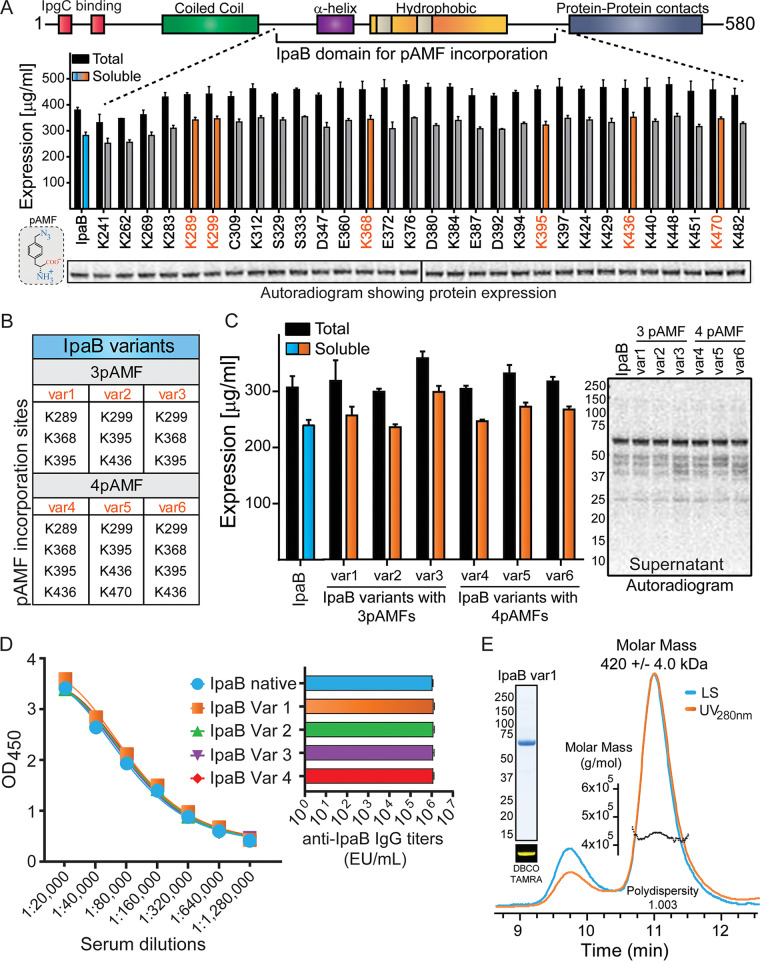
FIG 2.
Design, expression, and biophysical characterization of nnAA-containing IpaB alone or after conjugation to OPS-DBCO. (A) Native sequence of full-length IpaB with modular architecture was utilized to generate single-site pAMF incorporation variants at the listed sites, spanning the core of the protein. Expression of native IpaB (blue) and each of the variants (gray/orange) was determined using [14C]leucine incorporation into the translating polypeptide followed by autoradiogram recording. (B) pAMF incorporation sites with minimal impact on protein expression were selected (orange) and combined to generate 3 pAMF (var1 to -3) or 4 pAMF (var4 to -6)-containing variants. (C) The expression of var1 to -6 relative to native IpaB was determined using [14C]leucine incorporation assay. Autoradiogram analysis of the recovered supernatants shows expression of all IpaB variants in comparison to native IpaB. (D) Four-parameter logistic (4PL) dose-response curves of absorbance values at 450 nm versus serum dilution factor (left panel), and ELISA serum IgG titers (right panel) comparing immune reactivities of native IpaB and IpaB variants using human Shigella convalescent-phase sera. Data represent mean titer (obtained from multiple dilutions tested) ± standard error of the mean; native IpaB versus IpaB variants, P > 0.74 by t test. (E) Safe-blue-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of purified IpaB-var1; selective labeling with DBCO-TAMRA fluorescent dye confirmed pAMF incorporation. SEC-MALS analysis of purified IpaB-var1 showed a monodisperse distribution with an estimated molar mass of 420 ± 4 kDa. var, variant.