Abstract
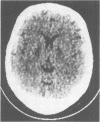
Ten days after an acute exposure to carbon monoxide, a 33-year-old woman exhibited severe chorea. CT scan revealed bilateral lucencies of the pallidum and anterior arm of the internal capsule. Chorea was successfully treated by chlorpromazine and did not relapse after treatment withdrawal. The mechanism of chorea in acute carbon monoxide poisoning is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruyn G. W., Padberg G. Chorea and systemic lupus erythematosus. A critical review. Eur Neurol. 1984;23(4):278–290. doi: 10.1159/000115743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I. S. Delayed neurologic sequelae in carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1983 Jul;40(7):433–435. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050070063016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver B., Norton S. Juvenile hyperactivity in rats after acute exposure to carbon monoxide. Exp Neurol. 1976 Jan;50(1):80–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEREUX J., CATOIR J. Deux complications nerveuses particulieres de l'intoxication par l'oxyde de carbone: syndrome parkinsonien transitoire avec inertie et mutisme et choree chronique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1952;86(1):40–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delouvrier J. J., Tritschler J. L., Dehen H., Nahum H. Aspect tomodensitométrique d'une intoxication oxycarbonée. Nouv Presse Med. 1979 Nov 26;8(46):3830–3830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destee A., Courteville V., Devos P. H., Besson P., Warot P. Computed tomography and acute carbon monoxide poisoning. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Mar;48(3):281–282. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.3.281-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A., Neu I. Ein Fall von Torsions-Dystonie nach Kohlenmonoxydvergiftung. Nervenarzt. 1977 Jun;48(6):345–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Stein R. W., Tanner C. M., Goetz C. G. A pure parkinsonian syndrome following acute carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1982 May;39(5):302–304. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510170044012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapresle J., Fardeau M. The central nervous system and carbon monoxide poisoning. II. Anatomical study of brain lesions following intoxication with carbon monixide (22 cases). Prog Brain Res. 1967;24:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton S., Culver B. A Golgi analysis of caudate neurons in rats exposed to carbon monoxide. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 2;132(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulst S. M., Walshe T. M., Romero J. A. Carbon monoxide poisoning with features of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1983 Jul;40(7):443–444. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050070073019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris S. Chorea caused by caudate infarction. Arch Neurol. 1983 Sep;40(9):590–591. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050080090021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Takahashi M., Ohashi N., Fusamoto H., Maemura K., Kobayashi H., Yoshioka T., Sugimoto T. Computerised tomography as an indication of long-term outcome after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):783–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Hennerici M., Wegener O. H. Delayed choreoathetosis following acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):98–99. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sills J. A., Vivori E., Rosenbloom L. Carbon monoxide poisoning: recovery associated with a transient dyskinetic syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 1974 Aug;50(586):519–520. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.50.586.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]