Figure 7. p53(A347D) mutants demonstrate enhanced tumorigenic capacity.
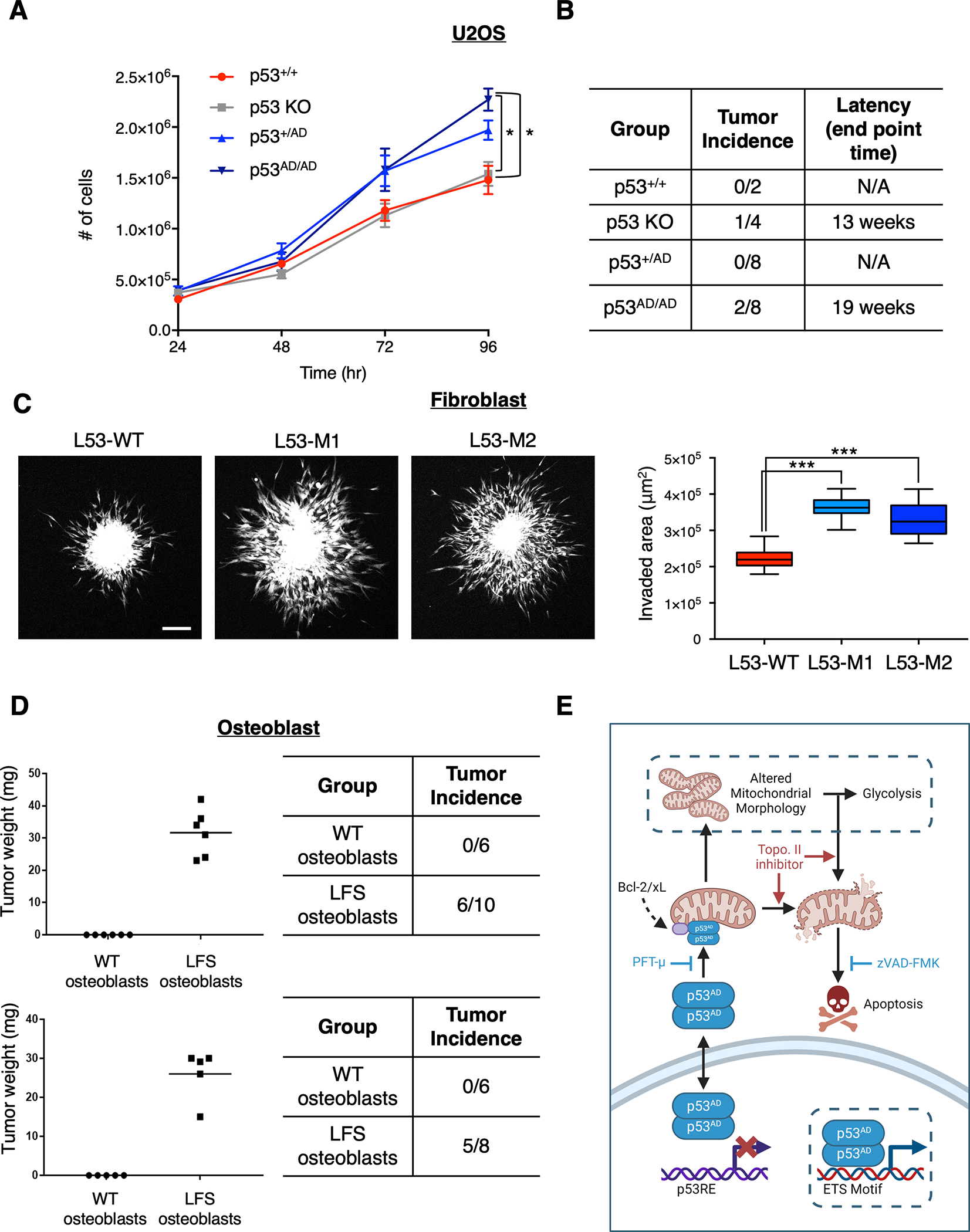
(A) The allelic series of U2OS cells were seeded at equivalent densities and counted at indicated timepoints. Data show relative cell number of indicated cell lines normalized to U2OS parental and represent mean ± SEM of three biologically independent experiments each with three technical replicates per condition.
(B) p53+/+, p53 KO, p53+/AD, and p53AD/AD U2OS cells were injected subcutaneously into the right and left dorsal flanks of NU/NU mice. Tumors were extracted at indicated end points post injection and weighed.
(C) Spheroids of primary dermal fibroblasts harboring either p53+/+ (L53-WT) or p53+/AD (L53-M1, L53-M2) were formed and implanted into a collagen matrix as described in Methods. Fluorescent microscopy images were taken 1 hour and 24 hours after implantation from which a representative confocal microscopy image (maximum projection) is shown (left) and invaded area was calculated by subtracting the area of initial spheroid from the ellipse covering the invaded area at endpoint of the experiments for each individual spheroid (right). The data is presented in a box plot depicting the median and second and third quartiles, with whiskers representing the data from 5% to 95%. Squares indicate mean values. Data was pooled from three biologically independent experiments and contains 24 spheroids for condition L53-WT, 28 spheroids for condition L53-M1, and 26 spheroids for condition L53-M2. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(D) WT and LFS iPSC-derived osteoblasts were injected subcutaneously into the right and left dorsal flanks of NU/NU mice. Tumors were extracted 1 month post injection and weighed (left). Table (right) demonstrates tumor incidence from two biologically independent experiments and indicates the number of injections per condition (n=2, 6–10 injections per group).
Statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed t-test. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05
(E) Model depicting novel activities of mutant p53(A347D). Dimer-forming p53(A347D) has lost the ability to bind and transactivate canonical p53 target genes yet gains the ability to bind select genes with ETS motifs, which may lead to their activation or repression. p53(A347D) can translocate to mitochondria and interact with anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, leading to apoptosis following topoisomerase ii inhibition. Although p53(A347D) induces mitochondrial network aberrations, it is yet unclear whether altered mitochondrial morphology is a result of either direct mitochondrial interactions or the novel transcriptional activity of dimeric mutant p53, which are denoted with dotted borders. Altered mitochondrial morphology and function may cause a compensatory increase in glycolysis. Model diagram was created using Biorender.com
