Fig. 8: UBXN2A protein levels predominantly upgrade during the early stage of tumor development and improve survival rates in colorectal cancer patients.
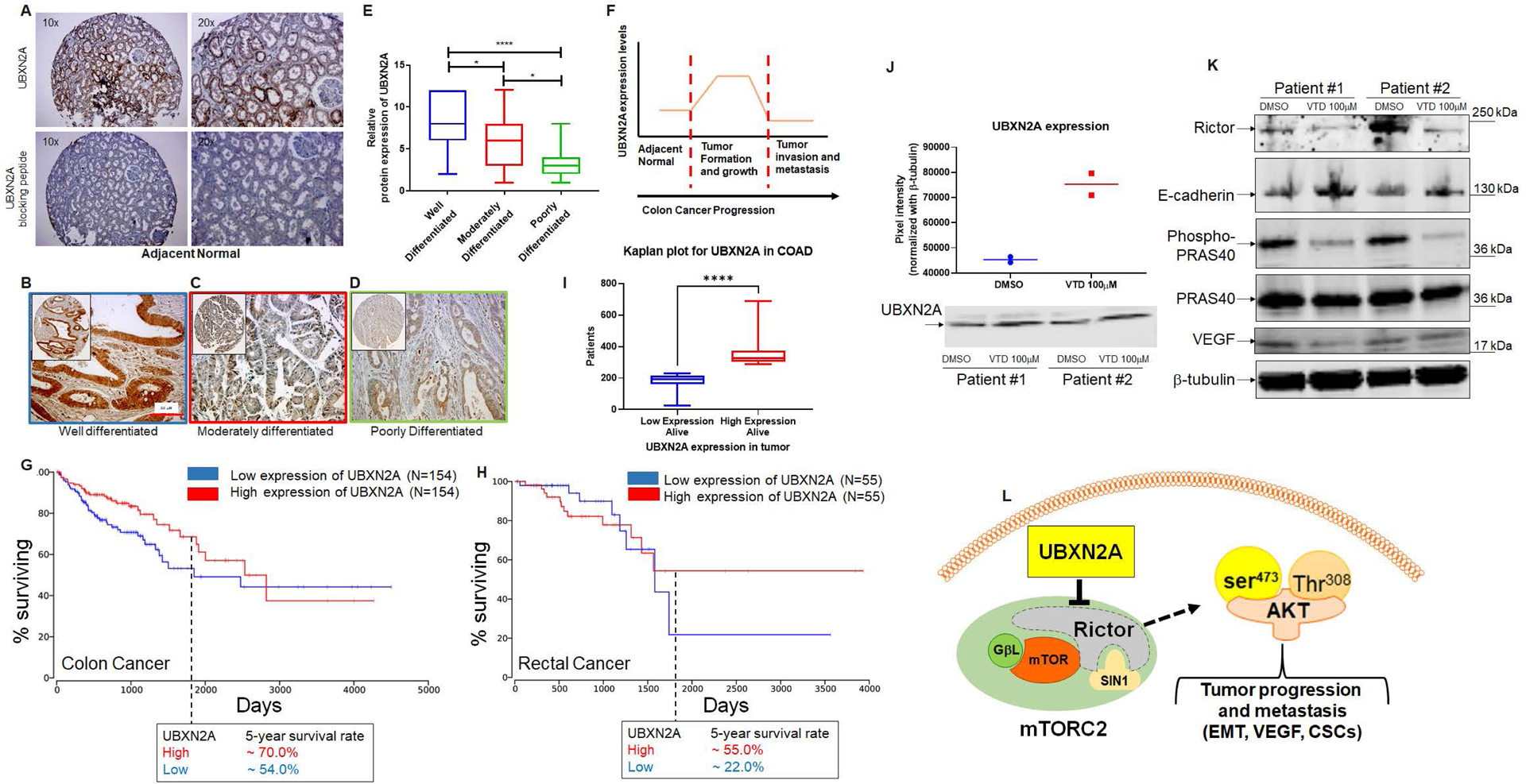
A shows UBXN2A’s medium protein expression level in normal colon tissues. A peptide-blocking assay confirmed the specificity of the antibody against the UBXN2A protein in the IHC study. B-D: IHC staining was used to stain cytoplasmic and nuclear UBXN2A in well-differentiated (n=26), moderately (n=74), and poorly differentiated (n=24 tumor tissues) human colon tumor tissues. E: UBXN2A expression levels of colon cancer tissues were manually scored. The quantitative scoring system revealed that UBXN2A, as a tumor suppressor protein, significantly upregulates in the early stage of colon cancer and shows a significant reduction in a higher stage of colon cancer. The reduction of UBXN2A is associated with a poorer prognosis in higher stages of CRC. (F). Kaplan–Meier’s analysis of extracted survival data from TCGA shows COAD, a subtype of colorectal cancer, indicates a correlation of higher survival rate with higher UBXN2A expression. The 5-year survival rate is ~20% higher than patients with low expression of UBXN2A in tumors (G). READ, a subtype of colorectal cancer Kaplan–Meier’s analysis, shows a favorable survival outcome in high UBXN2A expression. Patients with rectal cancer with a high level of UBXN2A show ~30% elevation of 5-year survival (H). Panel G and H were produced using the Human Protein Atlas and ONCL tools. For ONCL, we used 33 low and 33 high percentiles parameters. Further analysis shows a significantly larger portion of alive patients with COAD had higher UBXN2A expression compared to lower expression of UBXN2A, indicating a longer progression-free survival than those with low UBXN2A in the TCGA (I). PDOs generated from surgically removed CRC tumors (n=2) were treated with the UBXN2A enhancer Veratridine (VTD, 100μM) for 72 hours. Two individual PDOs showed VTD elevates the level of UBXN2A protein expression by approximately two-fold (J) and simultaneously decreases Rictor resulting in alteration of mTORC2 protein targets, including reduction of P-PRAS40 and VEGF proteins as well as elevation of E-cadherin (K). Schematic diagram showing the mechanistic inhibitory action of UBXN2A on mTORC2 tumorigenic pathway through selective proteasomal degradation of Rictor protein. The absence of a fully functional mTORC2 complex leads to the inhibition of several downstream metastatic pathways (L).
