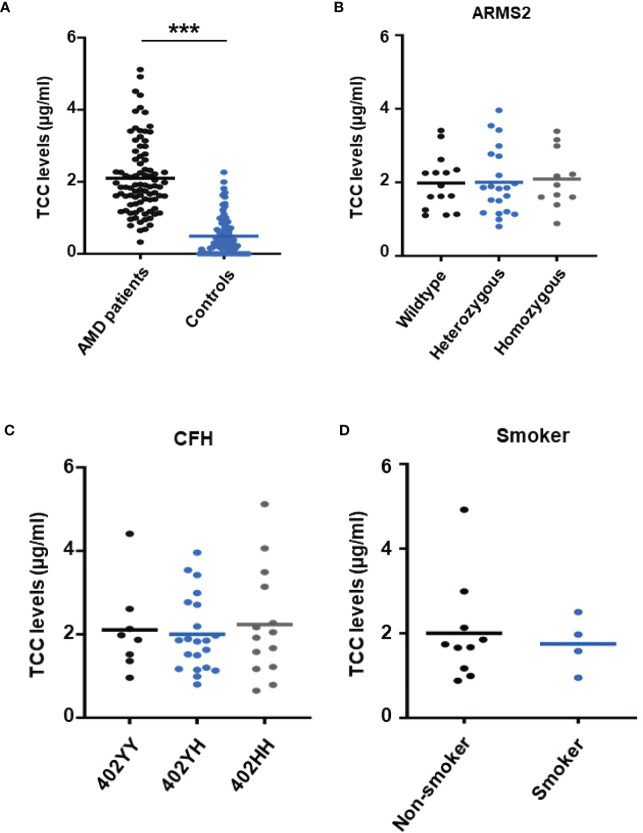
Figure 1.
Plasma levels of terminal complement complex (TCC) in plasma from healthy donors and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) patients with AMD risk alleles. (A) Plasma levels of TCC (µg/ml) in AMD patients (n = 87) vs. healthy controls (n = 86) showing significantly higher TCC levels in AMD patients (p < 0.001). (B) TCC levels stratified for Age-related maculopathy-susceptibility 2 (ARMS2) risk alleles, with all patients carrying one Complement factor H (CFH 402YH) risk allele. No significant difference in TCC levels among patients with no (wild type (WT), n = 15), one (heterozygous, n = 21), and two (homozygous, n = 11) ARMS2 risk alleles existed. (C) TCC levels stratified for CFH risk alleles, with all patients carrying one ARMS2 risk allele. No significant difference in TCC levels among patients with no (CFH 402YY, n = 8), one (CFH 402YH, n = 21), and two (CFH 402HH, n = 14) CFH risk alleles. The horizontal lines represent the means of the TCC levels. ***p < 0.001 (Mann–Whitney U test). (D) TCC levels stratified for the risk factor smoking and non-smoking among patients who do not carry one of the investigated genetic risk alleles. As the “heterozygous patients” are heterozygous for CFH (CFH 402YH) and ARMS2, the same set of plasma samples from these patients was used for the comparison with homozygous deficient CFH (B) and ARMS2 (C) as well as with respective WT plasma.