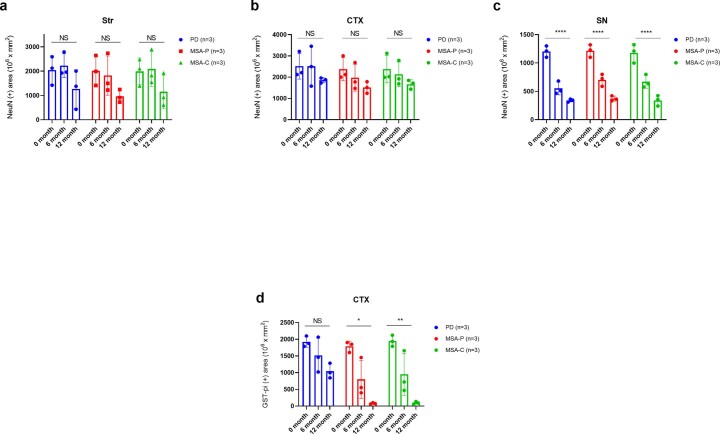
Extended Data Fig. 4. MSA-seeds induce oligodendrocyte degeneration compared with PD-seeds in the injected mouse brains.
α-synuclein seeds derived from the serum of PD or MSA cases were injected into the mouse striatum. The total area of the NeuN-positive neurons was quantified chronologically for (a) Str (n = 3: PD, p = 0.2282; MSA-P, p = 0.1409; MSA-C, p = 0.2306), (b) CTX (n = 3: PD, p = 0.411; MSA-P, p = 0.1465; MSA-C, p = 0.1953), and (c) SN (n = 3: PD, p < 0.0001; MSA-P, p < 0.0001; MSA-C, p < 0.0001). The total area of the Gst-pi-positive oligodendrocytes was quantified chronologically for (d) CTX (n = 3: PD, p = 0.053; MSA-P, p = 0.017; MSA-C, p = 0.003). Horizontal axis: time after α-synuclein seed injection; vertical axis: total area of NeuN-positive neurons or GST-pi-positive oligodendrocytes (μm2) per unit area (mm2). Data are represented as mean area per region ± SEM, n = 5 mice per group. Statistical analysis was conducted using two-sided one-way analysis of variance, resulting in significances of p < 0.0001 (****), p < 0.01 (**) and p < 0.05 (*) among each group. CTX, cortex; MSA, multiple system atrophy; MSA-C, MSA cerebellar variant; MSA-P, MSA Parkinsonian variant; NS, not significant; PD, Parkinson’s disease; SN, substantia nigra; Str, striatum.