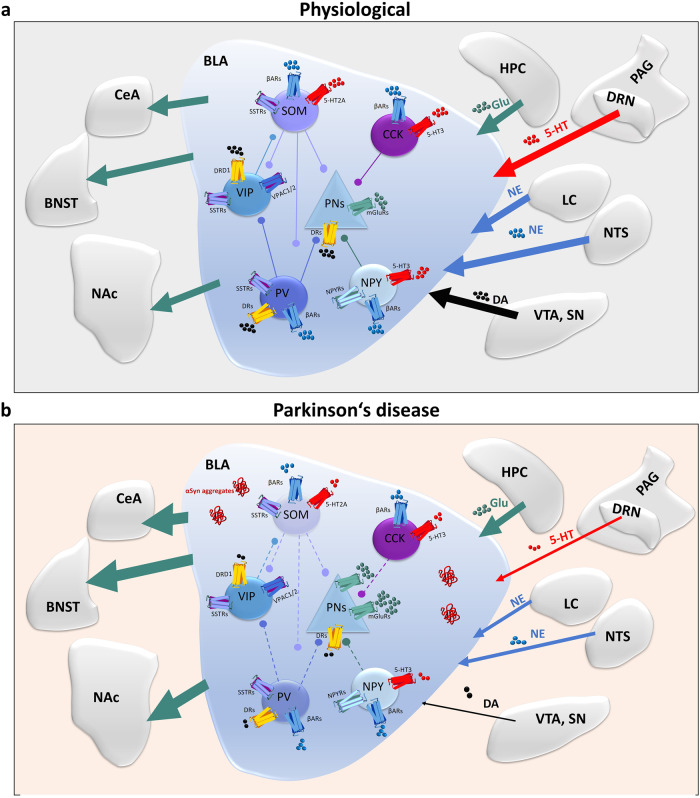
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram illustrating the physiology and proposed pathophysiology of the neuronal circuitry in Parkinson’s disease.
a Connectivity matrix among GABAergic neurons in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and the major neural inputs/output to or from BLA. β-adrenergic receptors (βARs), serotonin receptors (5-HT3, 5-HT2A), dopamine receptors (DRD1 or DRs), somatostatin receptors (SSTRs), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors (VPAC1/2) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are expressed differently on interneurons. Interaction of principal neurons (PNs) and five subtypes of interneurons expressing somatostatin (SOM), vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), cholecystokinin (CCK), parvalbumin (PV), and neuropeptide Y (NPY) contributing to the regulation of anxiety. The excitatory output of PNs determines the fear response and is mainly reduced by the local interneuron network. PNs and interneurons receive multiple inputs: the serotonergic projection from DRN/PAG and glutamatergic projection from HPC, the NE projection from LC and NTS, and the dopaminergic projection from VTA and SN, while PNsreleases glutamate to NAc, BNST, and CeA. Depending on how PNs and interneurons are shifted in activity, these circuitries are involved in the regulation of fear response and memory. b Model for the pathophysiology of the neuronal circuitry of increased fear in PD. When αSyn aggregates are present, distinct activation patterns emerge in the glutamatergic (principal neurons) and GABAergic (5 types of interneurons) neurons in BLA. The inputs from VTA/SN, NTS, LC, DRN/PAG to BLA change. The reduction of dopamine produced from the VTA/SN pathway results in a decrease in a long-term depression on PNs175 but also in altered interconnections between interneurons expressing DRs. The decrease in norepinephrine and serotonin projection also contributes to changes in neuronal activity in the BLA176. In addition, interneurons could be more prone to neurotoxicity of αSyn aggregates98 leading to disinhibition of PNs. As a result, the output of glutamate increases (or increased glutamatergic activity and hyperexcitability) from BLA, triggering increased fear behavior177,178. Serotonin: 5-HT 5-hydroxytryptamine, GABA gamma-aminobutyric acid, DA dopamine, Glu glutamate, VTA ventral tegmental area, SN substantia nigra, LC locus coeruleus, PAG periaqueductal gray, DRN dorsal raphe nucleus, HPC hippocampus, NAc nucleus accumbens, BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, CeA central amygdala.