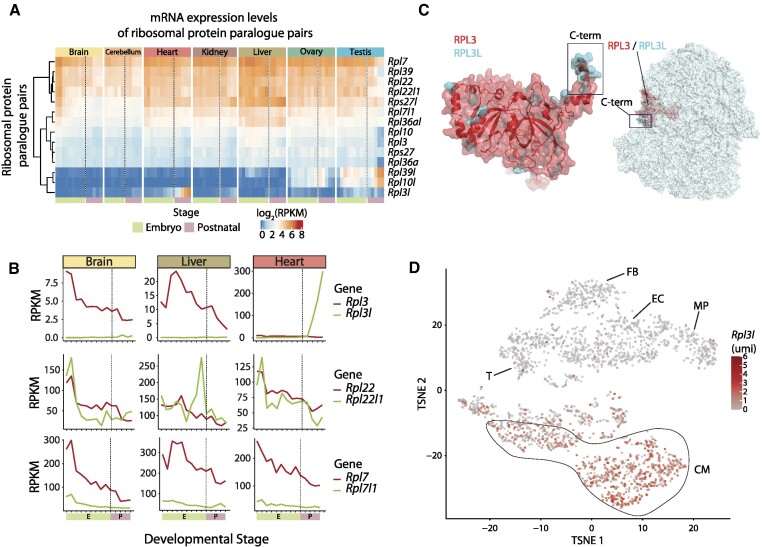
Figure 1.
RPL3L (uL3L) is a vertebrate RP paralogue with restricted tissue and developmental expression patterns, such as post-natal expression in mouse cardiomyocytes. (A) Heatmap of mRNA expression levels (log RPKM) of ribosomal proteins and their respective paralogues across embryonic (green: E10.5, E11.5, E12.5, E13.5, E14.5, E15.5, E16.5, E17.5 and E18.5) and post-natal mice tissues (pink: P0, P3, P14, P28 and P63). Processed data (RPKM) were obtained from Cardoso-Moreira et al. (40). See also Supplementary Figure S7 for a heatmap containing all RPs. (B) mRNA expression levels of ribosomal paralogue pairs (RPKM) in three different tissues (brain, liver and heart) for Rpl3/Rpl3l (upper panel), Rpl22/Rpl22l1 (middle panel) and Rpl7/Rpl7l1 (bottom panel). The developmental stages, shown on the x-axis, have been coloured depending on whether they correspond to embryonic (green) or post-natal (pink) stages. (C) Structural alignment of human RPL3 (red) and RPL3L (uL3L) (cyan); the C-terminus is highlighted (left) as is the location of RPL3 (uL3)/RPL3L (uL3L) within the ribosome (right). The C-terminus of RPL3 (uL3) and RPL3L (uL3L) is located at the surface of the ribosome, whereas the N-terminus of both proteins lies closer to the peptidyltransferase centre (PTC). The ribosome structure has been obtained from the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human 80S ribosome, corresponding to PDB code 6IP5 (101), which includes RPL3. The Homo sapiens RPL3L (uL3L) structure was obtained from the ModBase (102) database and structurally superimposed to the RPL3 structure in the 80S ribosome. (D) T-distributed stochastic neighbour embedding (T-SNE) plot depicting Rpl3l expression across mouse heart cell types. Expression data have been extracted from publicly available single-cell RNA-seq data from Ren et al. (60). Each dot represents a cell. Expression levels are shown as umi (unique molecular identifiers). Abbreviations: CM, cardiomyocytes; EC, endothelial cells; FB, fibroblasts; MP, macrophage; T, T cells.