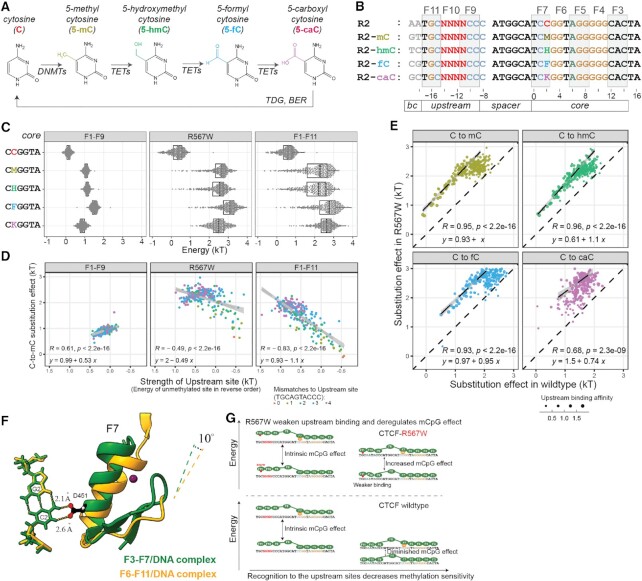
Figure 4.
The methylation effect of CTCF recognition is negatively regulated by the strength of upstream sites. (A) Known cytosine methylation and modification pathways in human. (B) Methyl-Spec-seq libraries design testing various C-to-xC effects at position 2 with altered upstream sites. Barcodes at –19 and –18 indicate the type of modifications. (C) Variants distribution of binding energy with different modifications and constructs; M, H, F, K are short for methylated, hemimethylated, formyl, and carboxyl cytosines respectively. (D) Relationship between observed C-to-mC substitution effects and the strength of upstream site, which is defined by the energy of corresponding unmethylated site. (E) Comparison of C-to-xC substitution effects between wildtype and R567W mutant constructs; The dashed lines indicate linear regression of high affinity sites (with energy of unmethylated sites below 0.4kT). (F) Structural comparison of existing CTCF-DNA complexes; Two structures were aligned over bases C2 and G2; Only CG at position 2 and finger 7 were shown. (G) Proposed Upstream Regulation model of CTCF.