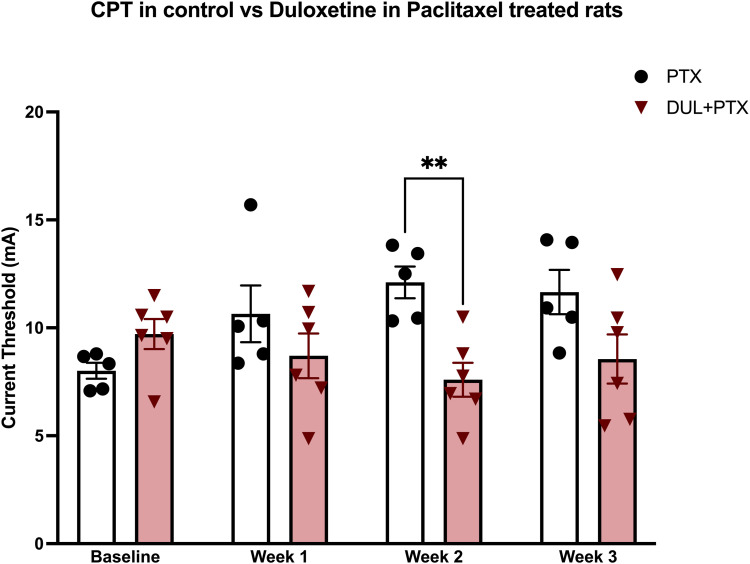
Figure 3.
One group of rats was treated with Paclitaxel (1 mg/kg i.p.), every other day for 4 treatments (PTX); a second group was treated with Duloxetine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) daily for 10 doses starting 3 days prior to the administration of the first dose of Paclitaxel (DUL + PTX). Compared to the PTX baseline, CPT for the PTX group was significantly increased after PTX treatment (one-way RM ANOVA, F(3, 12) = 5.8, *p = 0.011). CPT for the DUL + PTX group was significantly different from that for the PTX group (two-way RM ANOVA, Interaction Factor F(3, 27) = 6.8, **p = 0.0015). Significant “time x treatment” interaction indicates that the difference between PTX and DUL + PTX groups was time-dependent and therefore cannot be just a result of vertical shift between groups (e.g., due to the difference in baselines). Pretreatment with Duloxetine significantly attenuated PTX-induced elevation of CPT at week 2 (Holm-Šídák’s multiple comparisons test, PTX vs DUL + PTX: Baseline, t(36) = 1.3, p = 0.3; Week 1, t(36) = 1.5, p = 0.3; Week 2, t(36) = 3.4, **p = 0.007; Week 3, t(36) = 2.3, p = 0.07). Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5 for PTX group and n = 6 for DUL + PTX group.