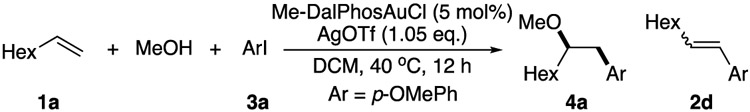
Table 1.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Variation from “standard conditions” | conv. (3a) | 4a | 2d |
| 1 | none | 100% | 95% (93%) | <5% |
| 2 | AgSbF6 | 100% | 73% | 25% |
| 3 | 60 °C | 100% | 65% | 30% |
| 4 | rt | 20% | 15% | <5% |
| 5 | DCB as solvent | 100% | 89% | 10% |
| 6 | MeOH as solvent | 50% | 45% | <5% |
| 7 | Add 1 eq. K3PO4 | 100% | 87% | 10% |
| 8 | Add 1 eq. KOAc | <5% | 0% | 0% |
| 9 | Mor-DalphosAuCl 5 mol% | 20% | 15% | <5% |
| 10 | No [Au] | 0% | - | - |
| 11 | No [Ag] | 0% | - | - |
| 12 | No ArI | No conversion on 1a | ||
| 13 | dppm(AuBr)2 10 mol%, ArB(OH)2, Selectfluor, MeCN/MeOH, 50 °C | 20% | ||
| 14 | PPh3AuCl 10 mol%, ArN2BF4, [Ir] cat. MeOH, rt, hv | 0% | ||
Conditions: 1a (0.4 mmol), MeOH (0.6 mmol), 3a (0.2 mmol), Au cat. (0.01 mmol), AgOTf (0.21 mmol), DCM (2 mL), 40 °C, 12 h.
1H NMR yields using 1,3,5-tribromobenzene as an internal standard (isolated yields).
