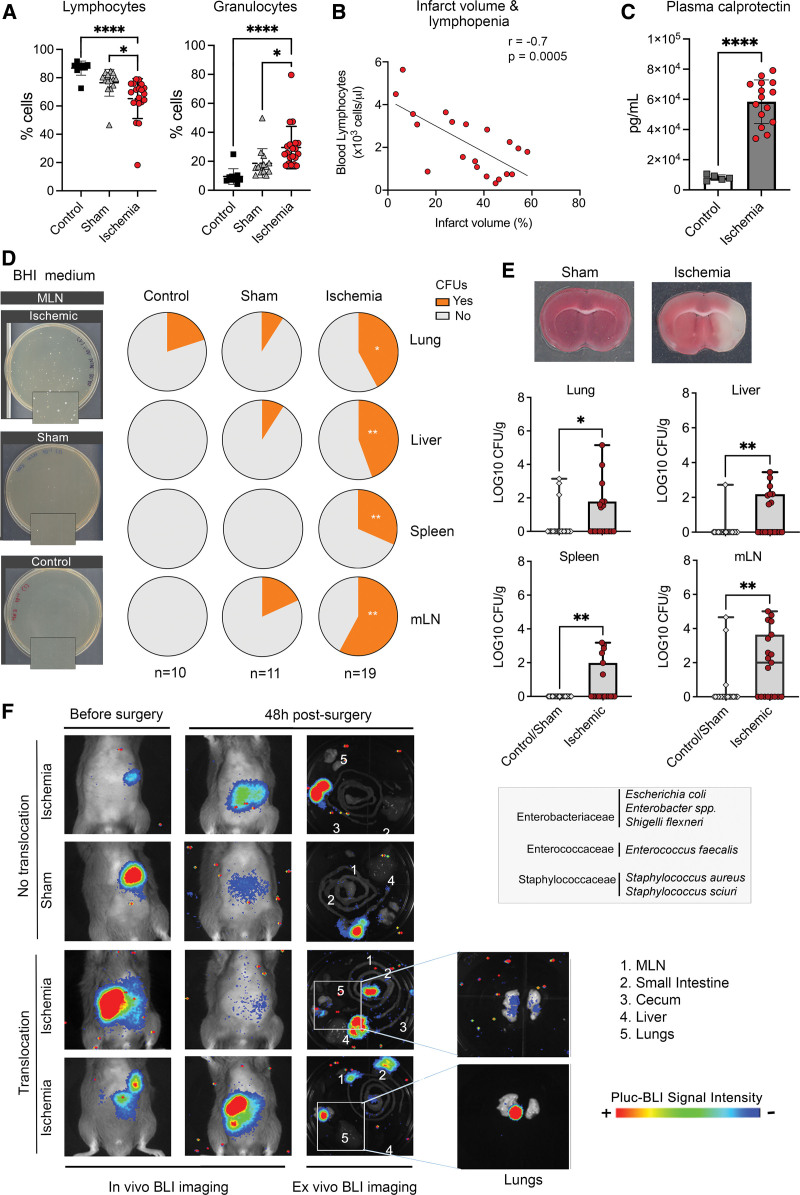
Figure 1.
Ischemia-induced immune depression and bacterial growth. Mice were studied 2 d after ischemia or sham operation, and controls. A, Ischemia (n=19) reduced blood lymphocytes vs sham (n=14; *P=0.011) and controls (n=10; ****P<0.0001), and increased granulocytes vs sham (*P=0.021) and controls (****P<0.0001); 1-way ANOVA/Šídák test). B, After ischemia, blood lymphocyte number was inversely correlated with lesion volume (Pearson r=−0.7, P=0.0005, n=19). C, Ischemia (n=15) increased plasma calprotectin levels vs controls (n=5; P=0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test). D, Illustrative images of brain heart infusion (BHI)-agar plates seeded with mesenteric lymph node (MLN) of ischemic (n=19), sham (n=11), and control (n=10) mice. Magnifications (2×) illustrate colony-forming units (CFUs) after ischemia. Quantification showed no differences between sham and controls (Figure S1D) and both groups were pooled together for comparison against ischemic mice. The proportion of mice with CFUs (Yes) in organs was higher in ischemic than sham/control (lung:*P=0.040; liver:**P=0.003; spleen:**P=0.005; mLN:**P=0.001; χ2). E, Representative brain section of sham and ischemic mice (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride [TTC] staining). Number of bacteria CFUs (mean±SD) of ischemic (n=19) vs sham/controls (n=21) showed more CFUs in lung (*P=0.046), liver (**P=0.005), spleen (**P=0.007), and mLN (*P=0.003; Mann-Whitney U test) of ischemic mice. List of bacteria identified in ischemic mice by 16S RNA gene partial sequencing. F, Mice received antibiotics followed by oral bioluminescent Escherichia coli before ischemia (n=10) or sham operation (n=6). At 48 h, bioluminescence was detected ex vivo in the lungs of 2 ischemic but none of the sham-operated mice. BLI indicates bioluminescence imaging.