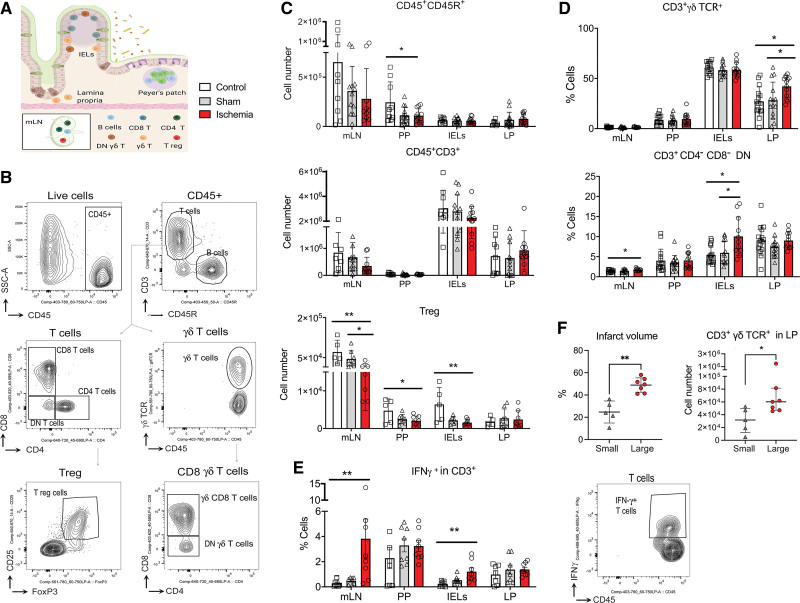
Figure 2.
Stroke induced a proinflamamtory shift in gut lymphocytes. A, Lymphocytes were obtained from mesenteric lymph nodes (mLN), Peyer Patches (PP), intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), and lamina propria (LP) from ischemic (n=12) and sham (n=14) mice 48 h postsurgery, and naive controls (n=15). Figure generated with Biorender.com. B, Gating strategy for flow cytometry analysis. C, Ischemia reduced B lymphocyte (CD45+CD45R+) number in PP (*P=0.018 vs control; 1-way ANOVA/Holm-Šídák test); CD3+ T cells showed a trend to reduction, and regulatory T cells (Tregs; CD4+CD25+forkhead box P [Foxp]3+) significantly decreased in mLN (**P=0.007 vs control; *P=0.041 vs sham; Kruskal-Wallis test/Dunn test), PP (*P=0.041 vs control), and the IELs (**P=0.006 vs control); 1-way ANOVA/Holm-Šídák test. D, Ischemia increased the % of CD3+ γδ T cell receptor (TCR)+ cells (*P=0.019 vs control and sham) in LP, and CD3+CD4-CD8- double-negative (DN) cells in mLN (*P=0.046 vs sham) and IELs (*P=0.033 vs control and sham); 1-way ANOVA/Holm-Šídák test. E, Representative cytometry plot of intracellular IFN (interferon)-γ (n=8 mice/condition). Ischemia increased vs control IFN-γ in CD45+CD3+ T cells in mLN (**P=0.003) and IELs (**P=0.002; Kruskal-Wallis test/Dunn test). F, Mice were dichotomized by the median of infarct volume in small (n=5) or large (n=7) groups (**P=0.0025, Mann-Whitney U test). Mice with larger infarcts had more CD3+γδ TCR+ cells in LP (*P=0.048; Mann-Whitney U test). Values are expressed as the mean±SD and all individual points are shown.