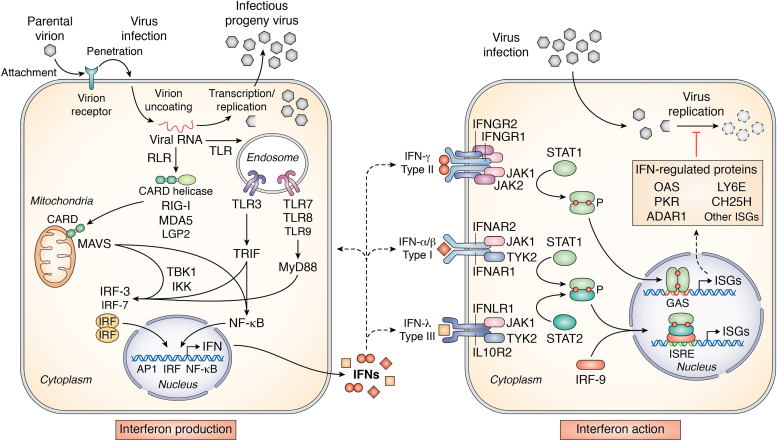
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram summarizing the interferon system response activated by virus infection leading to interferon production (left) and interferon action (right). The IFN-producing cell shown on the left illustrates a cell induced to synthesize IFN in response to virus infection. The cytoplasmic RLR MDA5 and endosomal TLRs sense viral (nonself) and possibly cellular (self) nucleic acids and signal via the mitochondrial adaptor MAVS and the TRIF and MyD88 adaptors, respectively, to activate the interferon regulatory (IRF) 3 and 7 and NF-κB transcription factors to transcriptionally activate IFN expression. The IFN-treated cell shown on the right depicts a cell induced to express IFN-regulated proteins by JAK-STAT signal transduction leading to transcriptional activation of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression. ISG expression in response to type I α/β/ω or type III λ IFN treatment occurs via ISRE element regulation, and type II γ IFN treatment via GAS element regulation. Among the ISGs implicated to play a role in the antiviral action of IFNs against SARS-CoV-2 virus are OAS1 2′5′-oligoadenylate synthetase, PKR protein kinase, LY6E lymphocyte antigen 6 and CH25H cholesterol 25-hydroxylase.