Fig. 3.
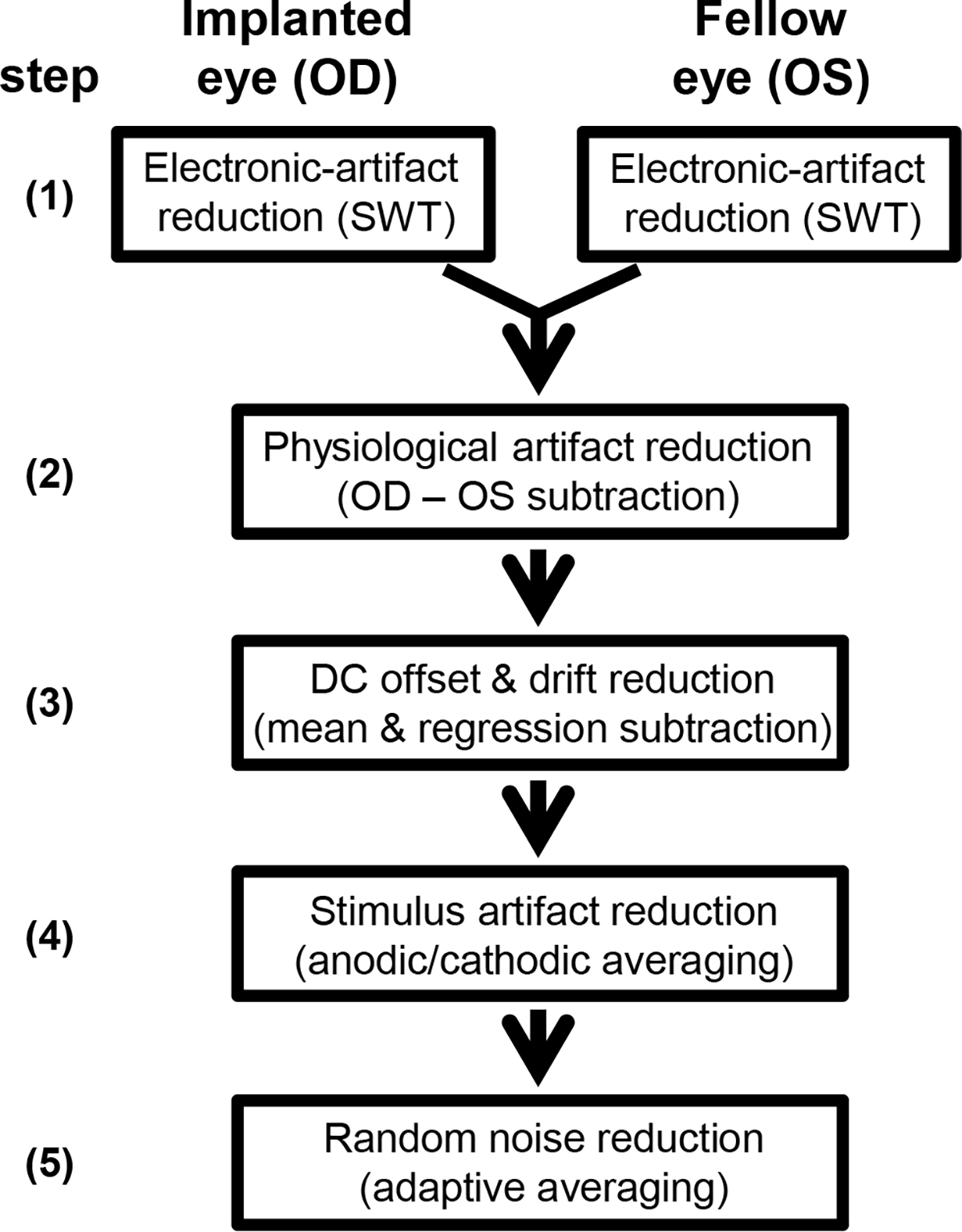
Flow chart of the signal processing steps of electrically evoked ERGs (eERGs) to reduce the stimulus artifact and noise. First, stationary wavelet transformation was applied to decrease the 120/s electronic artifact. OD and OS responses were then subtracted correcting for physiological artifacts. Resulting epochs were corrected for DC offset and drift using simple linear transformations. Stimulus artifacts were reduced by averaging of anodic-first and cathodic-first stimuli. Lastly, adaptive averaging was used to decrease signal noise by including low-noise epochs and reject those with large movement artifacts.
