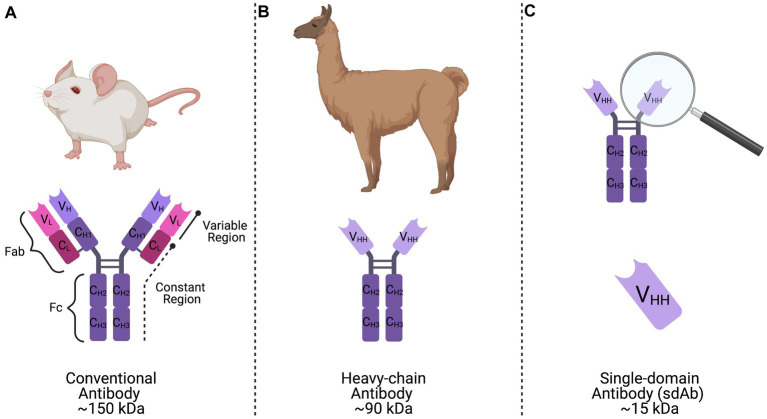
Figure 1.
Representation of conventional, heavy-chain, and single-domain antibodies. (A) Conventional mammalian antibodies are comprised of a basic structure consisting of two variable and constant heavy chains and two variable and constant light chains forming the antigen binding fragment (Fab) region, as well as two constant heavy chains forming the crystallizable fragment (Fc) region. (B) Camelid heavy-chain antibodies are composed of two identical constant heavy chains and a variable region (VHH) linked by a curved hinge that is responsible for antigen-binding activity. (C) A single-domain antibody (sdAb) is the single antigen binding domain of camelid heavy-chain antibodies, or the VHH region, that has been synthetically produced and retains full functionality.