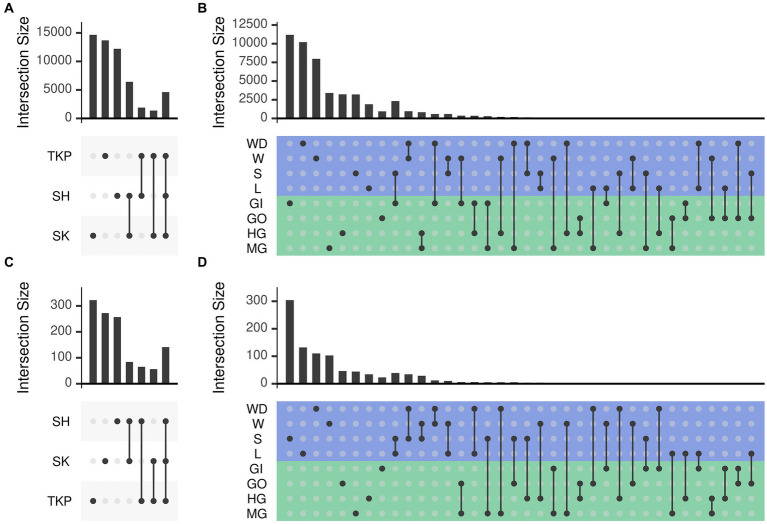
Figure 4.
Number of ASVs shared across sampling sites and sample types. The number of ASVs in common (namely simultaneously detected with abundance higher than zero) between different sets was reported following the upset representation. This representation is conceptually similar to a Venn diagram, but intersections are reported as a matrix instead of using different shapes depending on the number of sets, which become very complex to understand with more than three or four sets. Panels a and b report the number of shared ASVs obtained from 16 s rRNA amplicon sequencing whereas panels b and d report those obtained from ITS1 sequencing. Set intersections were displayed in a matrix layout where each row is a different site (panels A and C) or sample type (panels B and D) and each column corresponds to a different intersection. In panels (B) and (D) the rows of the matrix were colored according to the sample type: green for crab’s organs and blue for environmental samples. Intersected sets are reported using points connected by a straight line. The number of ASVs contained in each intersection is reported using bars on top of the intersection considered. Intersections are mutually exclusive so that if an ASV is present in a given intersection it is excluded from the others. Sites and sample types were abbreviated as follows: TKP, To Kwa Peng; SK, Sai Keng; SH, Shui Hau; MG, midgut; HG, hindgut; GO, gonads; GI, gills; L, litter; S, soil; W, water; WD, water debris.