Abstract
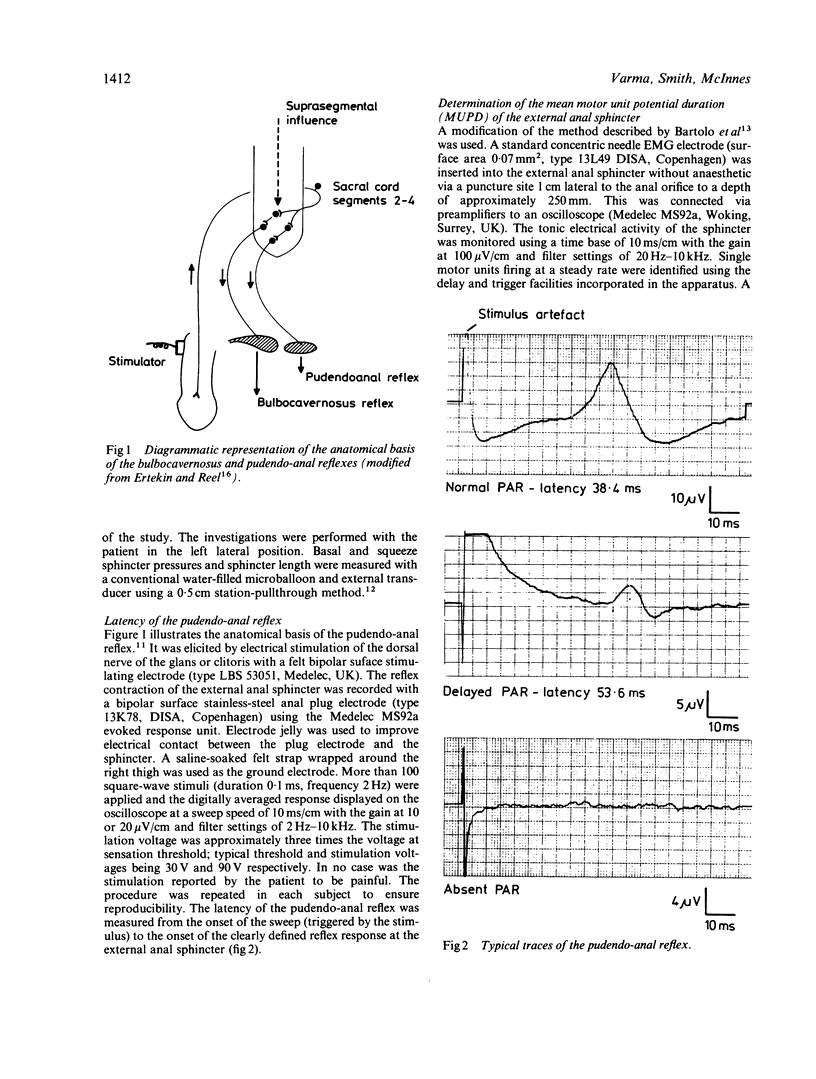
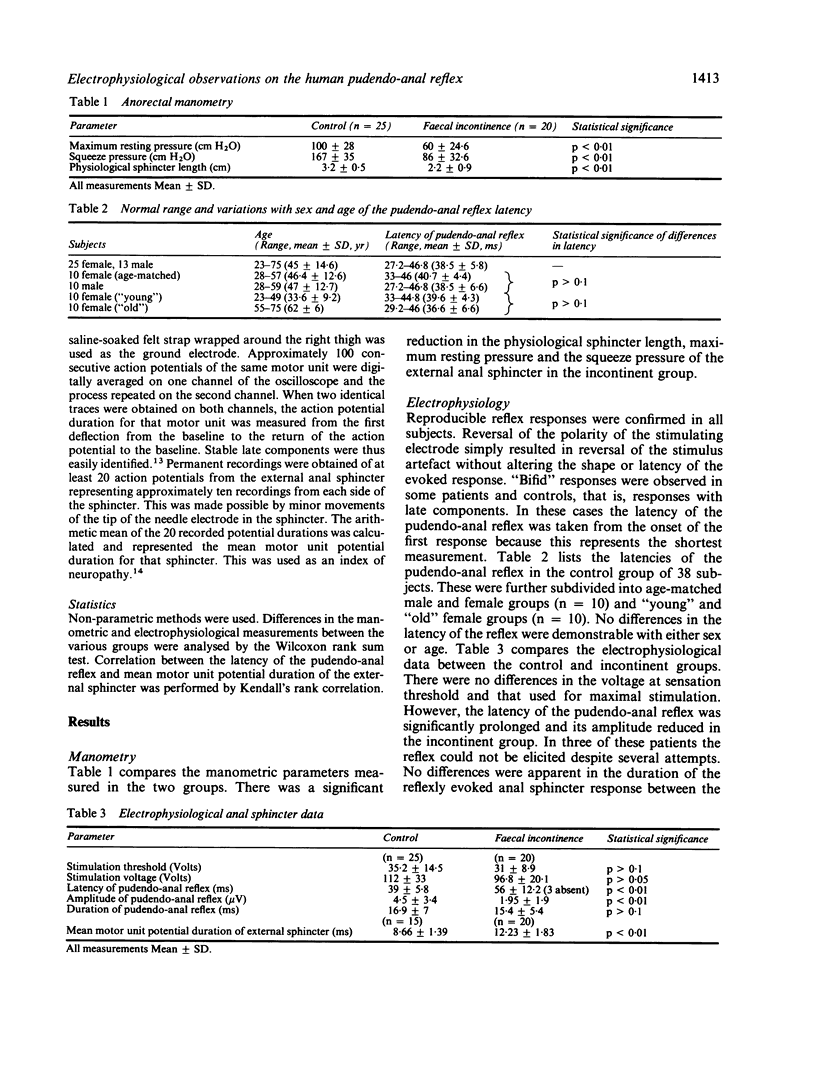
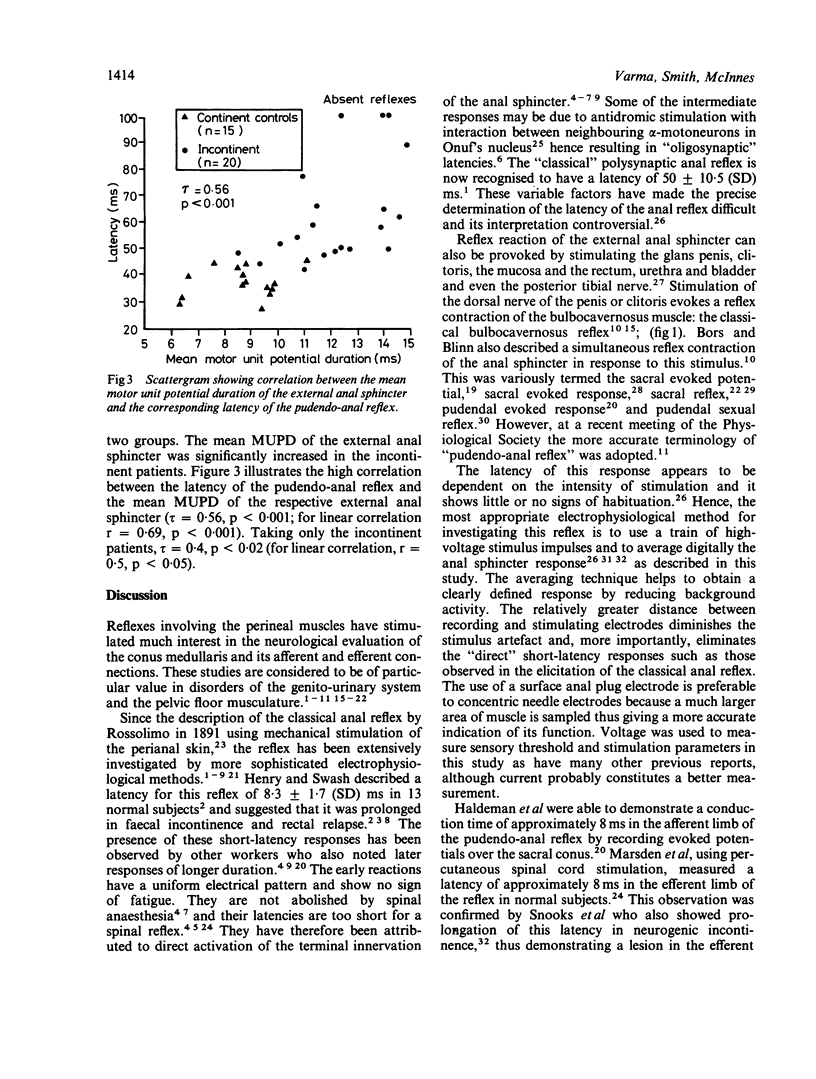
A reproducible electrophysiological technique is described to determine the latency of reflex contraction of the external anal sphincter in response to stimulation of the dorsal genital nerve: the pudendo-anal reflex. This was studied in 38 asymptomatic control subjects and 20 women with neurogenic faecal incontinence, supplemented by determination of the mean motor unit potential duration (MUPD) of the external anal sphincter and anorectal manometry. The reflex latency in the control group was 38.5 +/- 5.8 (SD) ms and appeared to be independent of age or sex. Three patients with faecal incontinence had absent reflexes; the remainder showed significant prolongation of latency (56 +/- 12.2 SD ms) and diminution of amplitude. MUPD was prolonged in incontinence and showed significant correlation with the corresponding reflex latency determination (tau = 0.56, p less than 0.001). The latency of this polysynaptic spinal reflex hence provides a reliable index of neuropathy of the external anal sphincter.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOBBITT J. M., LAPIDES J. Diagnostic value of bulbocavernous reflex. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Nov 3;162(10):971–972. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.72970270002010a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORS E., BLINN K. A. Bulbocavernosus reflex. J Urol. 1959 Jul;82(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)65843-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHTHAL F., PINELLI P. Action potentials in muscular atrophy of neurogenic origin. Neurology. 1953 Aug;3(8):591–603. doi: 10.1212/wnl.3.8.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolo D. C., Jarratt J. A., Read N. W. The cutaneo-anal reflex: a useful index of neuropathy? Br J Surg. 1983 Nov;70(11):660–663. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800701106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolo D. C., Jarratt J. A., Read N. W. The use of conventional electromyography to assess external sphincter neuropathy in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Dec;46(12):1115–1118. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.12.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilkey W. J., Awad E. A., Smith A. D. Clinical application of sacral reflex latency. J Urol. 1983 Jun;129(6):1187–1189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52632-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick H. C., Bradley W. E., Scott F. B., Timm G. W. Pudendal sexual reflexes. Electrophysiologic investigations. Urology. 1974 Mar;3(3):376–379. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(74)80129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertekin C., Reel F. Bulbocavernosus reflex in normal men and in patients with neurogenic bladder and/or impotence. J Neurol Sci. 1976 May;28(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertekin C., Reel F., Mutlu R., Kerküklü I. Bulbocavernosus reflex in patients with conus medullaris and cauda equina lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Apr;41(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidas A., Galloway N. T., McInnes A., Chisholm G. D. Neurophysiological measurements in primary adult enuretics. Br J Urol. 1985 Dec;57(6):635–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1985.tb07022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway N. T., Chisholm G. D., McInnes A. Patterns and significance of the sacral evoked response (the urologist's knee jerk). Br J Urol. 1985 Apr;57(2):145–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1985.tb06408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway N. T., Tainsh J. Minor defects of the sacrum and neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Br J Urol. 1985 Apr;57(2):154–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1985.tb06410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogan P., Gueritaud J. P., Horcholle-Bossavit G., Tyc-Dumont S. Direct excitatory interactions between spinal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):755–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldeman S., Bradley W. E., Bhatia N. N., Johnson B. K. Pudendal evoked responses. Arch Neurol. 1982 May;39(5):280–283. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510170022006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry M. M., Swash M. Assessment of pelvic-floor disorders and incontinence by electrophysiological recording of the anal reflex. Lancet. 1978 Jun 17;1(8077):1290–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiff E. S., Swash M. Normal proximal and delayed distal conduction in the pudendal nerves of patients with idiopathic (neurogenic) faecal incontinence. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;47(8):820–823. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.8.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane R. J., Siroky M. B. Studies on sacral-evoked potentials. J Urol. 1980 Dec;124(6):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Merton P. A., Morton H. B. The latency of the anal reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;45(9):857–857. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.9.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. E., Parks A. G., Swash M. Physiological studies of the anal sphincter musculature in faecal incontinence and rectal prolapse. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):531–536. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDERSEN E. Studies on the central pathway of the flexion reflex in man and animal. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand Suppl. 1954;88:1–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen E., Harving H., Klemar B., Tørring J. Human anal reflexes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;41(9):813–818. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.9.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen E., Klemar B., Schrøder H. D., Tørring J. Anal sphincter responses after perianal electrical stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;45(9):770–773. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.9.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockswold G. L., Bradley W. E. The use of evoked electromyographic responses in diagnosing lesions of the cauda equina. J Urol. 1977 Oct;118(4):629–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)58131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushworth G. Diagnostic value of the electromyographic study of reflex activity in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1967;(Suppl):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siroky M. B., Sax D. S., Krane R. J. Sacral signal tracing: the electrophysiology of the bulbocavernosus reflex. J Urol. 1979 Nov;122(5):661–664. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snooks S. J., Henry M. M., Swash M. Anorectal incontinence and rectal prolapse: differential assessment of the innervation to puborectalis and external anal sphincter muscles. Gut. 1985 May;26(5):470–476. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.5.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swash M. Early and late components in the human anal reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;45(9):767–769. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.9.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma J. S., Smith A. N. Anorectal profilometry with the microtransducer. Br J Surg. 1984 Nov;71(11):867–869. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800711122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereecken R. L., De Meirsman J., Puers B., Van Mulders J. Electrophysiological exploration of the sacral conus. J Neurol. 1982;227(3):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00313567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodusek D. B., Janko M., Lokar J. Direct and reflex responses in perineal muscles on electrical stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jan;46(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. L., Williams N. S., Gibson J. S., Neal D. E., Morrison J. F. Electrically evoked activity in the human external anal sphincter. Br J Surg. 1985 Jan;72(1):38–41. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


