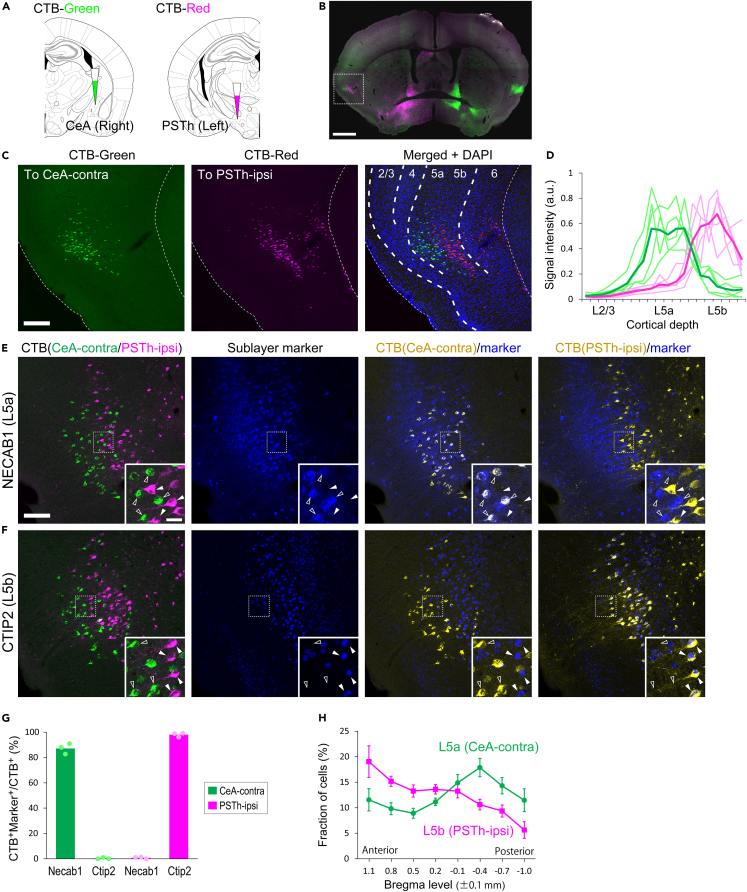
Figure 2.
Sublaminar and regional distribution of anatomically distinct cell populations in L5 of the insula
(A) Illustrations depicting dual-color CTB injections into the right CeA and left PSTh.
(B) A typical example of the confocal image of a coronal section containing CTB-labeled cells in the insula.
(C) Higher magnification views of the left insula (boxed region in B).
(D) Relative fluorescence intensities (arbitrary unit) of CTB labeling across cortical depth in the DgI (L2/3 to L5b). Note that the density of labeled cells across cortical depth can be estimated by the averaged fluorescence because of the localized fluorescence to cell somas. The signal intensities of CTB-green-labeled cells (projecting to the CeA-contra) and CTB-red-labeled cells (projecting to the PSTh-ipsi) are shown in green and magenta, respectively. Light colors represent individual mice (n = 5 mice with dual CTB injections), and dark colors are the means.
(E) Fluorescent images of a section containing CTB-labeled cells with immunostaining of NECAB1 (an L5a marker, blue). CeA-contra-projecting CTB-labeled cells (open arrowheads) but not PSTh-ipsi-projecting CTB-labeled cells (solid arrowheads) are immunopositive for NECAB1.
(F) Fluorescent images of a section containing CTB-labeled cells with immunostaining of CTIP2 (an L5b marker, blue). PSTh-ipsi-projecting CTB-labeled cells (solid arrowheads) but not CeA-contra-projecting CTB-labeled cells (open arrowheads) are immunopositive for CTIP2.
(G) The proportion of anatomically distinct CTB-labeled cell populations positive for the sublayer-specific molecular markers. Dots represent individual mice. Bars indicate the means (87.1% for NECAB1/CeA-contra; 0.33% for CTIP2/CeA-contra; 0.75% for NECAB1/PSTh-ipsi; 98.1% for CTIP2/PSTh-ipsi, n = 3 mice).
(H) The fraction of CeA-contra-projecting CTB-labeled cells (L5a population, green) and PSTh-ipsi-projecting CTB-labeled cells (L5b population, magenta) at eight locations across the A-P axis of the DgI. The A-P level of the maximum proportion is 0.4 ± 0.1 mm posterior to Bregma for the L5a population (Dunnett’s test, p < 0.05 [versus −0.1 ± 0.1 mm]; p < 0.01 [versus −0.7 ± 0.1 mm]; p < 0.001 [versus 1.1, 0.8, 0.5, 0.2, −1.0 ± 0.1 mm], n = 6 mice) and 1.1 ± 0.1 mm anterior to Bregma for the L5b population (Dunnett’s test, p < 0.01 [versus 0.8 ± 0.1 mm]; p < 0.001 [versus 0.5, 0.2, −0.1, −0.4, −0.7, −1.0 ± 0.1 mm], n = 5 mice). Error bars represent standard deviations. Scale bars: 1 mm (B), 0.2 mm (C), 0.1 mm (E), 20 μm (inset in E). See also Figures S2 and S3.