Fig. 4.
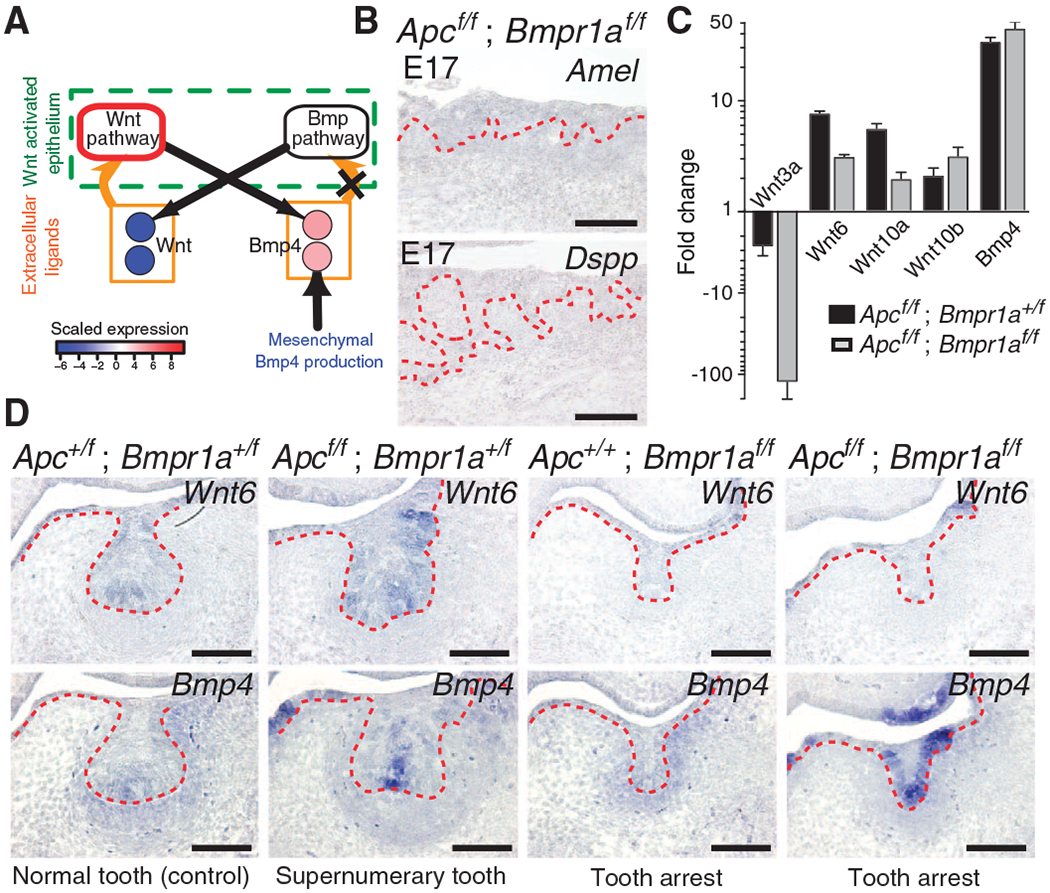
Loss of Bmpr1a signaling breaks the Wnt-Bmp circuit and prevents tooth formation induced by constitutive epithelial Wnt signaling. (A) Epithelial Bmpr1a loss of function (X) breaks the odontogenic circuit and results in decreased expression of genes encoding canonical Wnt ligands. The Wnt pathway node outlined in red represents constitutive Wnt pathway activity. (B) Sagittal sections at E17.5 in compound epithelial Apc loss-of-function; Bmpr1a loss-of-function (Apcf/f; Bmpr1af/f) mutants reveal undetectable Amel and Dspp expression and failure of tooth differentiation. The epithelium is denoted by the dashed red lines. n = 3 nonadjacent sections. (C) At E14.5, qRT-PCR reveals decreased Wnt3a, Wnt6, and Wnt10a expression in Apcf/f; Bmpr1af/f compared to epithelial Apc loss-of-function (Apcf/f; Bmpr1a+/f) mutants. Expression of Wnt10b was similar in Apcf/f; Bmpr1af/f and Apcf/f; Bmpr1a+/f. Data are means ± SD (n = 6; two biological replicates run in technical triplicate) normalized to Hprt. (D) Decreased epithelial Wnt6 expression in Apcf/f; Bmpr1af/f compared to Apcf/f; Bmpr1a+/f mutants in E14.0 coronal sections. Similar epithelial expression of Bmp4 in Apcf/f; Bmpr1af/f compared to Apcf/f; Bmpr1a+/f mutants. n = 3 nonadjacent sections. Scale bars, 200 μm (B) and 100 μm (D). See also figs. S15 to S17.
