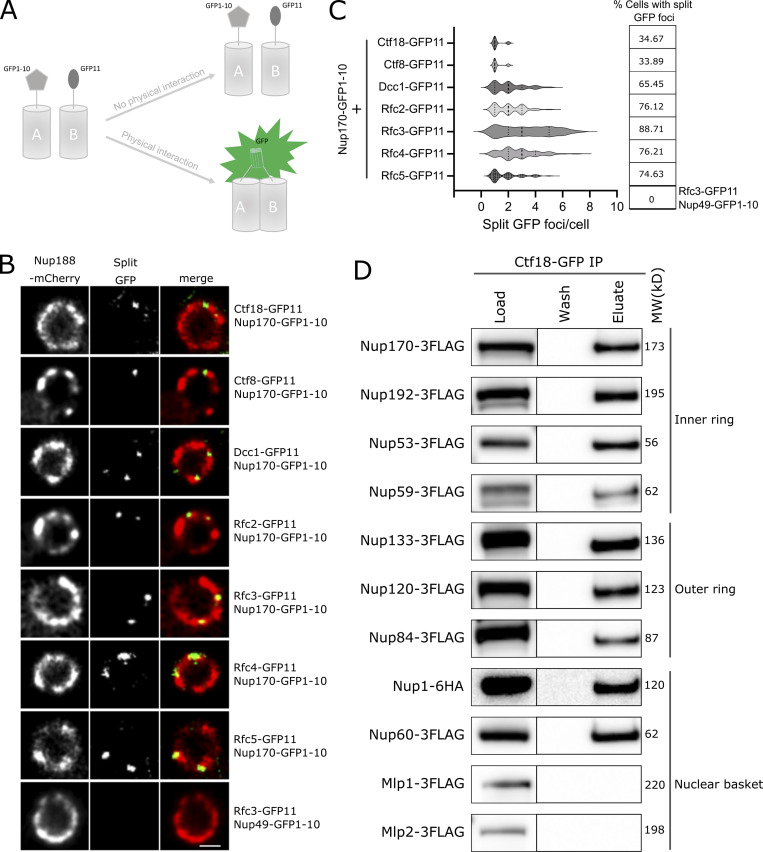
Figure 3.
Ctf18-RFC is recruited to a subset of NPCs lacking the nuclear basket nucleoporins Mlp1 and Mlp2. (A) Schematic showing the principle of the split-GFP assay. GFP1-10 and GFP11 are fused to proteins A and B, respectively, and when A and B interact, GFP1-10 and GFP11 associate to form a full-length GFP that can fluoresce. (B) Images of the nuclei of cells co-expressing Nup170–GFP1-10 and GFP11 tagged components of the Ctf18-RFC complex. The bottom panel image shows a cell co-expressing Nup49–GFP1-10 and Rfc3-GFP11. In these cells, the NPCs are marked by Nup188-mCherry. Single plane images from the acquired z-stacks are shown. Scale bar = 1 µm. (C) Violin plots showing the number of split GFP foci per cell for strains expressing Nup170–GFP1-10 and GFP11 tagged components of the Ctf18-RFC complex. The table on the right shows percentages of cells containing split GFP foci for the corresponding strains in the violin plots. The split GFP foci were not detected in cells co-expressing Nup49–GFP1-10 and Rfc3-GFP11 (bottom row of the table). (D) Ctf18-GFP fusion protein was affinity-purified from cell lysates containing 3FLAG-tagged nucleoporins or Nup1-6HA. Eluates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies to detect indicated nucleoporins. MW, molecular weight. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F3.