Figure 3. Effects of compression on cell signaling and death-related cellular outputs of nucleus pulposus cells.
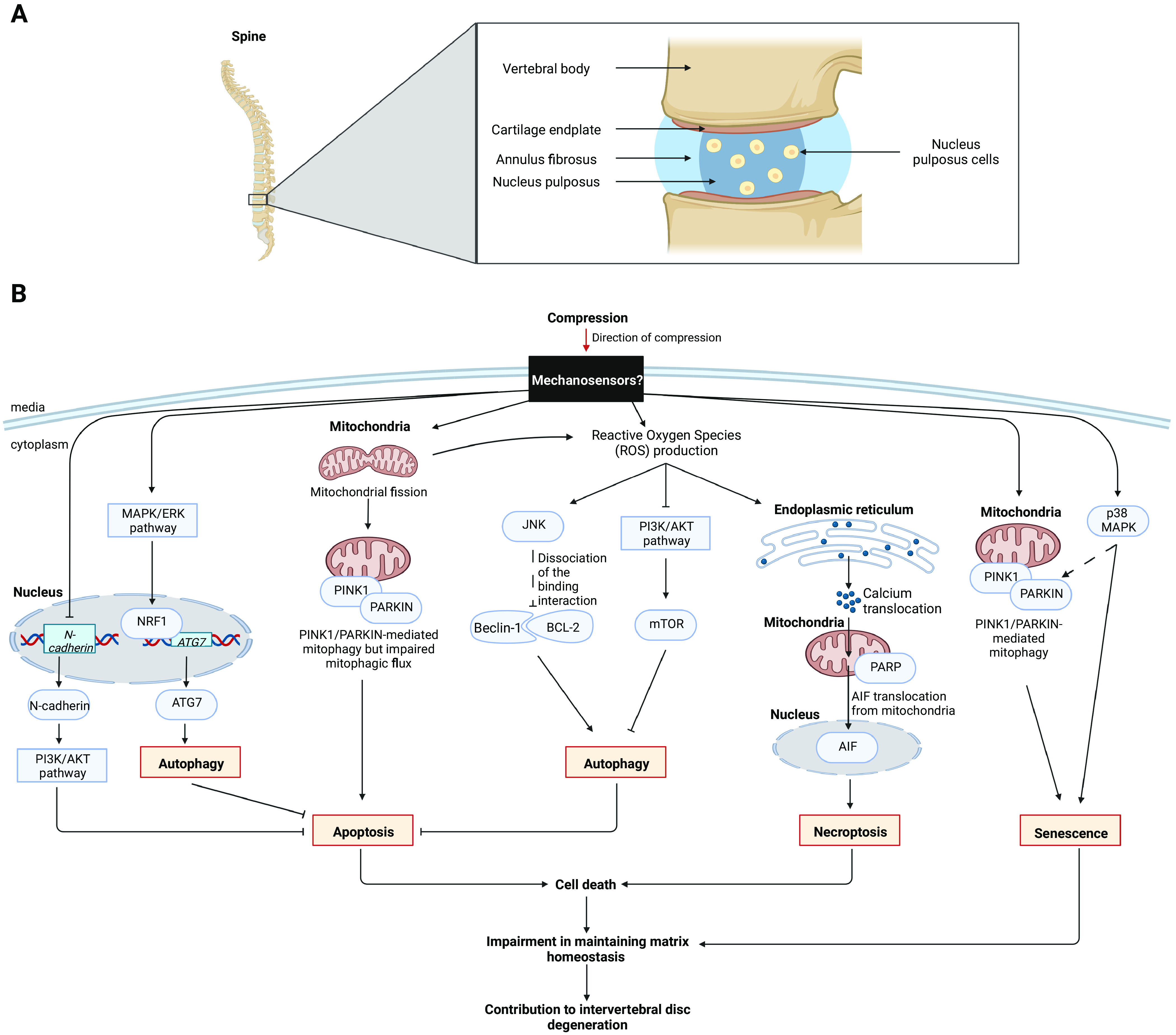
(A) Intervertebral disc structure. (B) Effects of compression in nucleus pulposus cells. Signaling pathways involved after compressive stress in nucleus pulposus cells. The activation of signaling pathways tightly regulate the balance between autophagy, cell death (apoptosis, necroptosis), and senescence in cells. The figure compiles data from Ma et al (2013), Li et al (2017, 2018, 2021b), Huang et al (2020), and Lin et al (2021). Undefined modulations are presented as dotted arrows. AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; ATG7, autophagy-related protein 7; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; N-cadherin, neural cadherin; NRF1, nuclear respiratory factor 1; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PINK1, PTEN (phosphatase and TENsin homolog)-induced kinase 1.
