FIGURE 3.
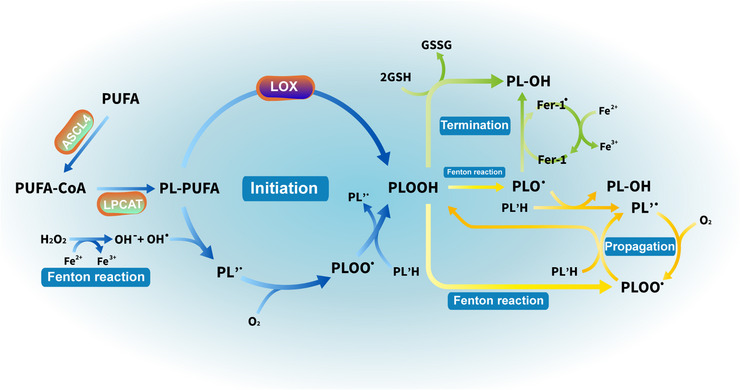
The three phases of lipid peroxidation. (i) Initiation is the process that generates radical compounds (PLOOH/PLOO•) from nonradical molecules (PL‐PUFA). (ii) Propagation, starting from lipid peroxides (PLOOH), is a peroxidative chain reaction giving rise to new radicals while the number of radicals remains constant. (iii) Termination is the process in which the peroxidative chain is broken by donating electrons to radical compounds so that transferring the active product (radical compounds) to a stable one (PL‐OH). It should be noted that the iron‐involved Fenton reaction, which participates in the process of initiation and propagation, is a free electron provider. PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty; ACSL4, acyl‐CoA synthetase long‐chain family member 4; PUFA‐CoA, coenzyme A‐activated polyunsaturated fatty acid; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; PL‐PUFA/PL/PL'H, phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids; LOX, lipoxygenase; PLOO•, phospholipid peroxy radical; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; PLO•, the phospholipid alkoxyl radical; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; Fer‐1, ferrostatin‐1; PL‐OH, phospholipid hydroxides.
