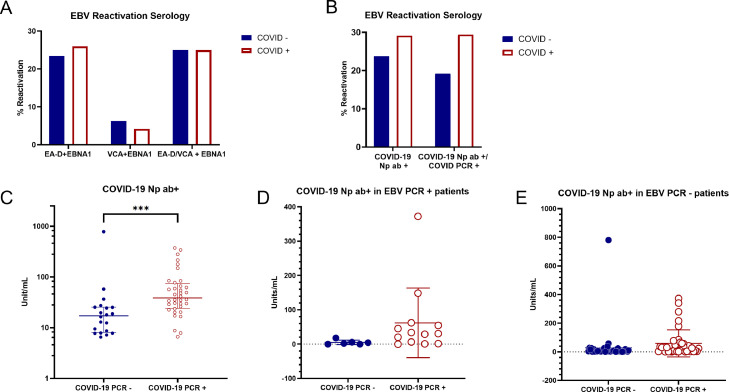
Fig. 3.
Detection of EA-D IgG and VCA IgM as determinants of EBV reactivation. A) Samples testing positive for the presence of EBV EA-D IgG and VCA IgM are charted as percentage of samples where EBV was reactivated among COVID negative and positive groups determined by PCR assay. Two sample proportion Z test: EBNA-1 and EA-D: p=0.3821, EBNA-1 and VCA: p=0.6593, EBNA-1 and EA-D/VCA: p=0.4519. B) Samples testing positive for the presence of either EBV EA-D IgG and VCA IgM, in addition to EBNA-1 IgG, are chartered as percentage of samples where EBV was reactivated among COVID negative and positive groups where COVID status was determined by the detection of COVID anti-nucleoprotein (COVID Np ab+) (left side) or detected by either PCR or detection of antibodies against nucleoprotein (right side). Two sample proportion Z test: COVID-19 positivity determined by Np seropositivity: p=0.2815, COVID-19 positivity determined by a positive PCR test or Np seropositivity: p=0.1588. C) Relative levels of antibodies against Np among COVID negative and COVID positive patients. COVID +/- groups on X-axis represent COVID determination by PCR test; therefore, COVID negative patients with detection of antibodies against Np demonstrate past infection. COVID status determined by PCR: p=0.0002 (Mann-Whitney test). *** represents p<0.001. D) Anti-Np IgG levels in EBV reactivated patients. Samples with antibodies against COVID Np were graphed for patients found to have reactivated EBV determined by detection of EBV genomes. EBV reactivation patients with current COVID determined by PCR had higher levels of antibodies against Np than EBV reactivating patients who had a past infection (p=0.066 Welch's t-test). E) Anti-Np IgG levels in EBV PCR negative patients. COVID PCR+ patients had higher levels of antibody against Np than COVID PCR – patients in the absence of EBV reactivation (EBV PCR-) (p=0.233 Welch's t-test).