Table 1.
Optimization of the C(sp2)─H Hydroxylation Using Hydrogen Peroxidea
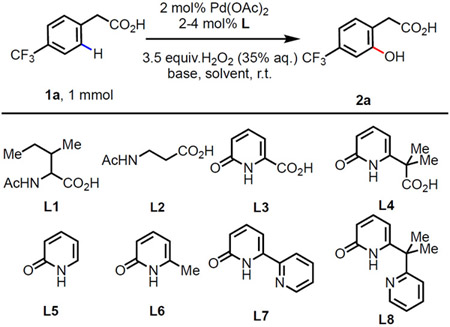
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Ligand | Base | Solvent | Yield (%) |
| 1b | L1 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 37 |
| 2 | L1 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
| 3 | L2 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
| 4 | L3 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
| 5 | L4 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 65 |
| 6 | L5 | K2HPO4 | DMA | trace |
| 7 | L6 | K2HPO4 | DMA | trace |
| 8c | L7 | K2HPO4 | DMA | <5 |
| 9c | L8 | K2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
| 10 | No L | K2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
| 11 | L4 | KHCO3 | DMA | 80 |
| 12 | L4 | K2HPO4 | CH3CN | 86 |
Conditions: 4-Trifluoro-phenylacetic acid (1.0 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (2 mol%), ligand (4 mol%), H2O2 (35% aqueous solution, 3.5 equiv.), base (1.5 equiv.) in solvent (3.0 mL) r.t., 24 h. Yields were determined by 1H NMR using CH3NO2 as the internal standard.
90°C.
2 mol% ligand.
