Figure 4.
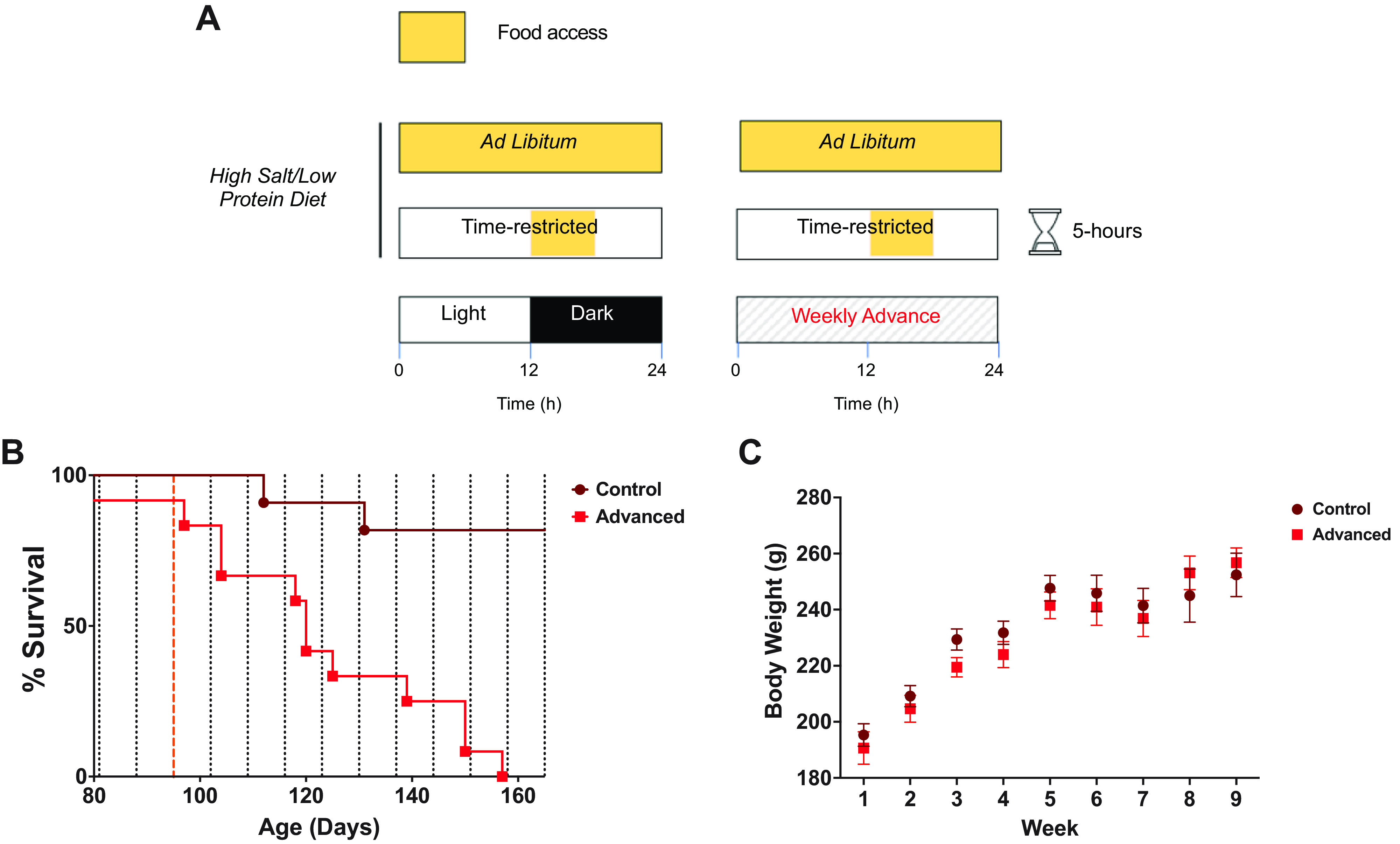
Time-restricted food access delays stroke onset but does not prevent environmental circadian disruption (ECD) effects. A: rats were fed a high-salt diet and water ad libitum. At the beginning of week 4, the water was switched to 1% salt water. Time-restricted feeding protocol allowed ad libitum access to food for 5 h during the same clock time daily as the rats in the regular light conditions regardless of their phase advancing schedule starting at 12 wk of age. B: while fixed time-restricted feeding lengthened life span overall, survival analysis showed a significantly longer life span of the control group (n = 12 rats) vs. the phase advancing group (n = 12 rats; log-rank Mantel–Cox test; P < 0.0001). C: body weights were similar across these 2 groups (2-way ANOVA; P = 0.1286) Dashed red line indicates the point at which water was switched to 1% salt water for all animals.
