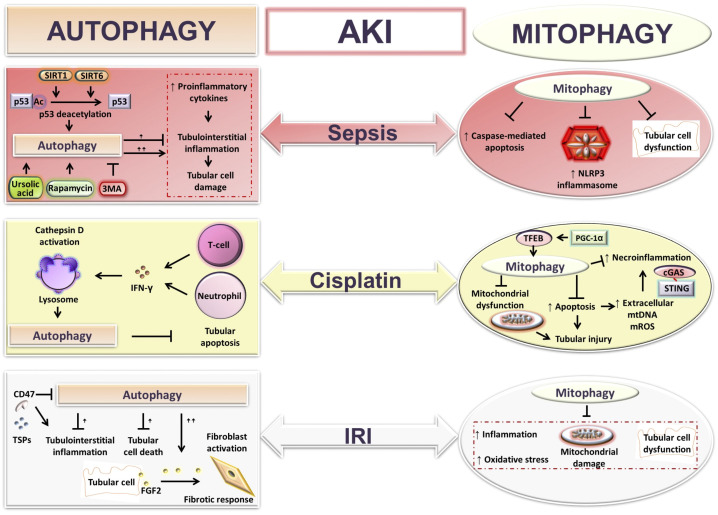
Figure 2.
Autophagy and mitophagy functions in acute kidney injury (AKI). Shown is a schematic presentation illustrating the roles of autophagy and mitophagy in various models of AKI: sepsis, cisplatin, and ischemia-reperfusion-injury (IRI)-mediated AKI. Autophagy and mitophagy protect against inflammation, tubular cell apoptosis, and kidney damage during AKI. However, an excessive autophagic response has been reported to promote inflammation, tissue injury, and AKI to CKD transition via fibroblast activation. cGAS, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; mROS, mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α; SIRT, sirtuin; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TFEB, transcription factor EB; 3MA, 3-methyladenine; TSP1, thrombospondin-1.