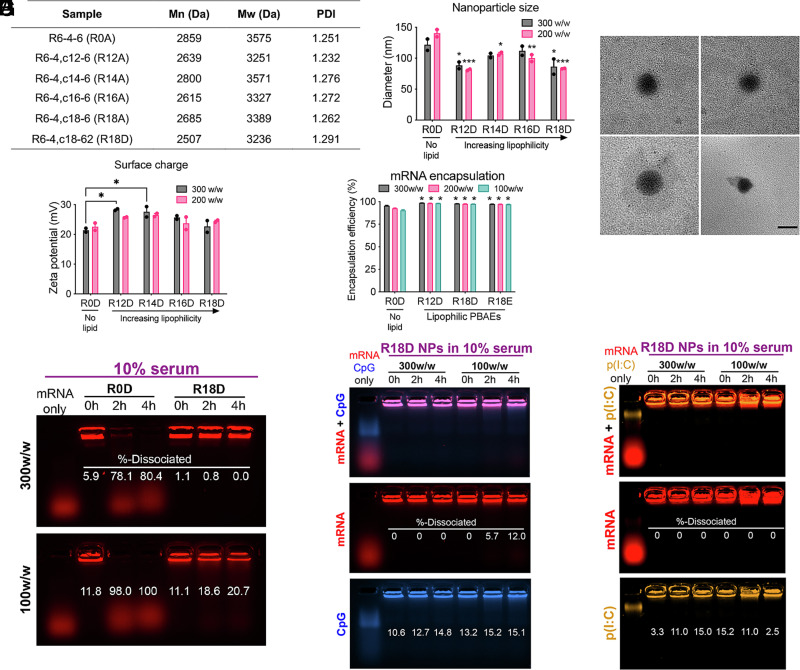
Fig. 2.
Characterization of bioreducible lipophilic poly(beta-amino ester) (PBAE) polymers and mRNA nanoparticles (NPs). (A) Molecular weights of PBAEs of varying lipophilicity assessed by GPC. (B) Hydrodynamic diameter of PBAE NPs formed at a 300 or 200 w/w ratio of polymer to mRNA assessed via DLS (n = 2). Significance indicates comparison to nonlipophilic PBAE nanoparticles (R0D) at the respective w/w ratio. (C) Representative TEM images of R18D mRNA NPs (Scale bar, 200 nm). (D) Surface charge of mRNA PBAE NPs in PBS (n = 2). (E) Encapsulation efficiency of mRNA assessed by the RiboGreen assay (n = 3). Significance indicates comparison to nonlipophilic PBAE nanoparticles (R0D) at the respective w/w ratio. (F) Encapsulation and dissociation of fluorescently labeled mRNA for nonlipophilic (R0D) and lipophilic (R18D) NPs formed at 300 and 100 w/w ratios after incubation in 10% serum over 4 h assessed by a gel electrophoresis assay. (G) mRNA and CpG ODN, (H) mRNA and poly(I:C) dissociation in 10% serum from R18D-based NPs formed at 300 and 100 w/w ratios over 4 h, respectively. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.