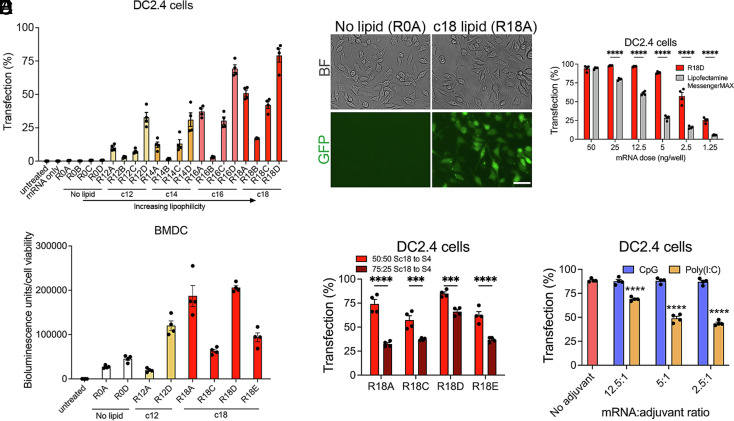
Fig. 3.
Transfection of dendritic cells (DCs) in vitro by bioreducible liphophilic PBAE mRNA nanoparticles (NPs). (A) Polymer library was evaluated for transfection of the murine dendritic cell line DC2.4 using mRNA encoding GFP. Cells were treated with NPs formed at 200 w/w and a dose of 50 ng mRNA/well, and transfection efficiency was assessed via flow cytometry after 24 h. (B) Representative bright-field (BF) and fluorescent microscopy images of DC2.4 cells transfected with nonlipophilic R0A or lipophilic R18A GFP mRNA NPs (Scale bar, 50 nm). (C) Transfection of DC2.4 cells by top-performing R18D NPs was assessed at various mRNA doses and compared to leading commercial mRNA transfection reagent Lipofectamine MessengerMAX. (D) A subset of the polymer library was evaluated on murine BMDCs using luciferase-encoding mRNA. Cells were treated with NPs at a dose of 25 ng mRNA/well, and bioluminescence activity was assessed after 24 h to determine transfection levels normalized to cell viability. (E) Polymers with the Sc18 monomer were synthesized with a 50:50 or 75:25 ratio of lipophilic side chain monomer Sc18 to hydrophilic side chain monomer S4. DC2.4 cells were treated with GFP mRNA NPs with varied lipophilicity at a dose of 25 ng mRNA/well, and transfection was assessed after 24 h. (F) The transfection efficiency in DC2.4s was examined following treatment with R18D NPs coencapsulating GFP mRNA and CpG or poly(I:C) adjuvants with varied mRNA to adjuvant ratios where the mRNA dose was kept constant (25 ng/well) after 24 h. Significance indicates comparison to no adjuvant control. Error bars represent SEM (n = 4). ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001.