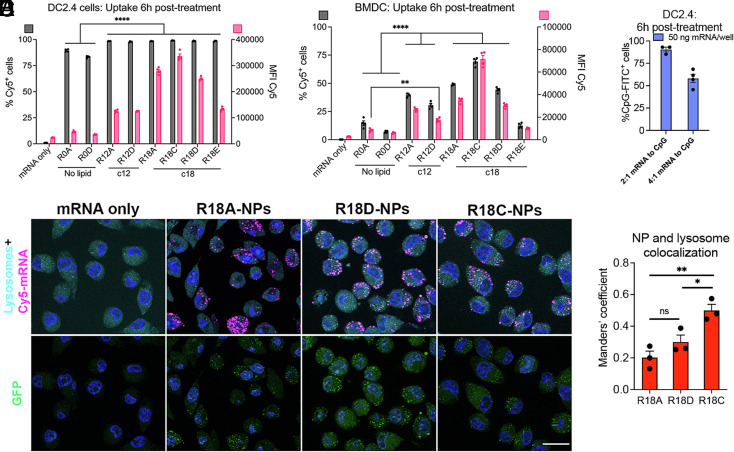
Fig. 4.
Cellular uptake and endosomal escape following mRNA nanoparticle (NP) design. (A) DC2.4 cells and (B) murine primary BMDCs were treated with NPs carrying Cy5-mRNA at a dose of 50 ng mRNA/well, and NP uptake was assessed at 6 h posttreatment by flow cytometry (n = 4). (C) DC2.4 cells were treated with R18D NPs coencapsulating mRNA at 50 ng mRNA/well and FITC-CpG, and uptake of CpG was assessed 6 h posttreatment by flow cytometry (n = 4). (D) Representative images of DC2.4 cells labeled with lysosome/endosome dye 6 h posttreatment with NPs carrying Cy5-labeled GFP-encoding mRNA to visualize cellular uptake, NP colocalization with endosomes/lysosomes, and GFP transfection (Scale bars, 20 μm). (E) Manders’ coefficient was determined using ImageJ to quantify the degree of colocalization between NPs and endosomes/lysosomes (n = 3). Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001.