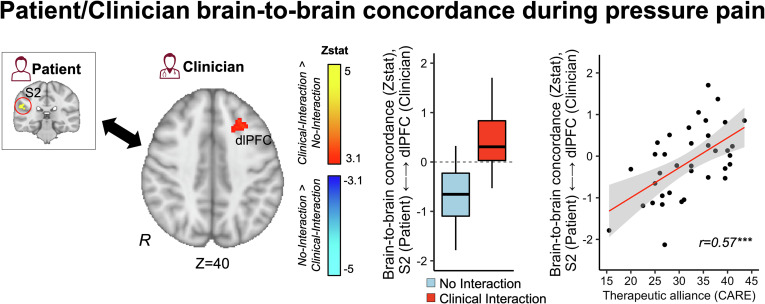
Fig. 5.
Patient/clinician concordance in brain activity during pain. In order to assess clinician concordance with patients’ pain-related brain activity during evoked pain, we first extracted the time series of the patient’s S2 activity from a cluster identified from an independent Solo fMRI scan run (Moderate pain–No pain). For each clinician’s fMRI data, we calculated the interaction term between the patients’ S2 time series and a binary function for the leg pressure stimuli. The outcome of this interaction term reflected the clinicians’ voxelwise time-dynamic concordance with the patient’s S2 activity during pain. For Clinical Interaction dyads, compared to No Interaction, clinicians showed increased dlPFC concordance with patients’ S2 activity (Left). The strength of S2-dlPFC concordance was positively correlated with therapeutic alliance (Right). ***P < 0.005.