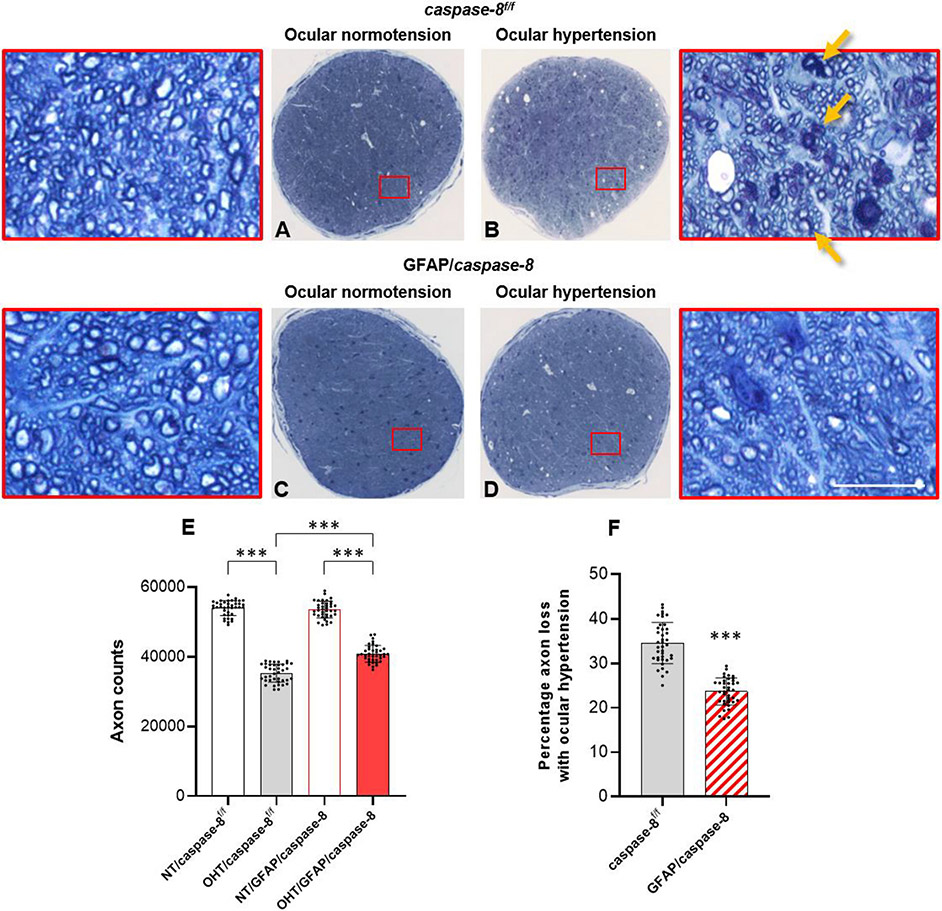
Fig. 4. Effects of GFAP/caspase-8 on optic nerve axon counts.
Presented are composite images of optic nerve cross-sections stained with 2% toluidine blue. Red boxed areas are shown in higher magnification (scale bar, 10 μm). Compared to normotensive caspase-8f/f control mice (A), there was a prominent axon loss and gliosis in ocular hypertensive eyes of caspase-8f/f controls (B). No alteration in optic nerve structure was detectable in normotensive mice with GFAP-targeting caspase-8 deletion (C). However, compared to ocular hypertensive caspase-8f/f controls, optic nerve structure was well preserved in ocular hypertensive eyes of GFAP/caspase-8 mice (D). E. The number of remaining axons was significantly higher in ocular hypertensive GFAP/caspase-8 mice than ocular hypertensive caspase-8f/f controls. F. Astroglial caspase deletion provided >30% protection against axon loss in experimental glaucoma. Yellow arrows show degenerating axons and myelin debris. Data (mean ± SD) represents 39 mouse eyes per group (***one-way ANOVA, P < 0.001).