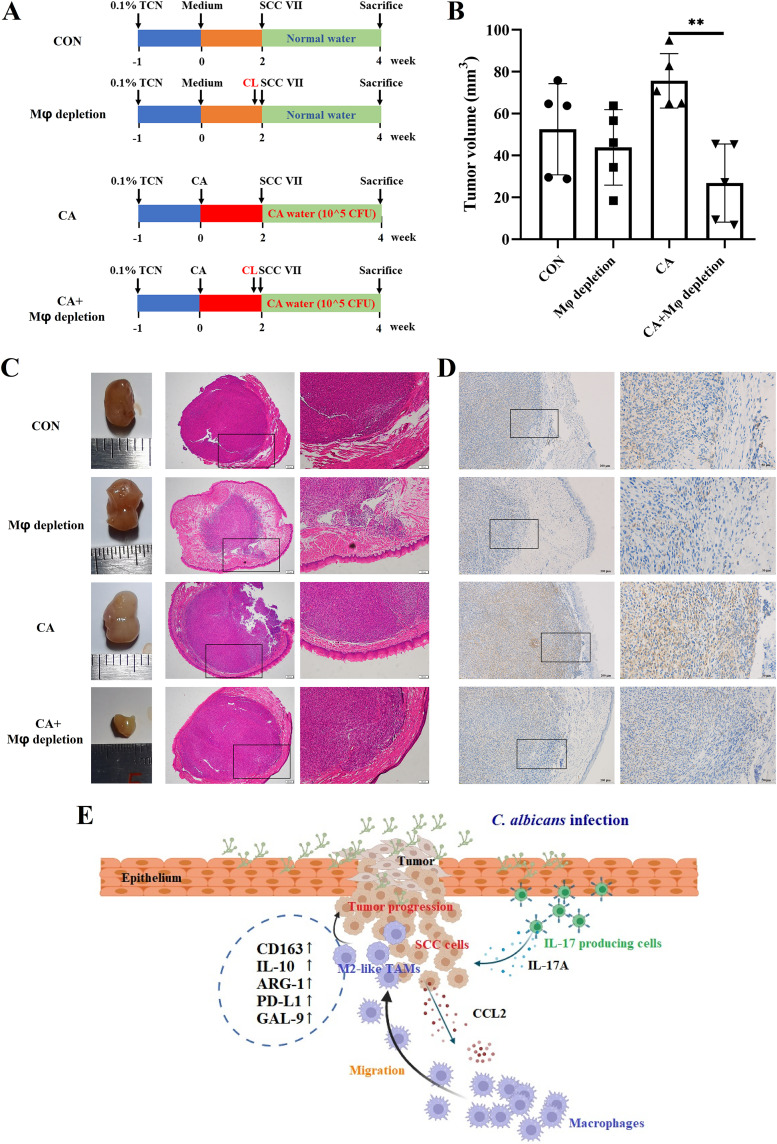
FIG 5.
The depletion of local macrophages alleviated the oral tumor progression promoted by C. albicans infection. (A) Schematic figure of local macrophage depletion experiment in C3H/HeN-SCC VII mice; CON (C3H/HeN-SCC VII), Mφ depletion (C3H/HeN-SCC VII with macrophage depletion), CA (C3H/HeN-SCC VII with C. albicans infection), and CA + Mφ depletion (C3H/HeN-SCC VII with C. albicans infection and macrophage depletion). (B) Tumor volume. (C) Representative tumor images and H&E images, scale bar = 200 μm or 100 μm. (D) Representative IHC images of F4/80; scale bar = 200 μm or 50 μm. (E) Mechanism diagram of this research (drawing with online software, https://app.biorender.com/, agreement number is FQ256A5VYW). C. albicans infection promoted IL-17A production and the following IL-17RA signal activation in oral tumor cells; then, tumor cells released CCL2 to attract macrophages into TME; the macrophages in TME showed an immunosuppressive phenotype with elevated expressions of PD-L1, GAL-9, and M2-like macrophage markers. **, P < 0.01.