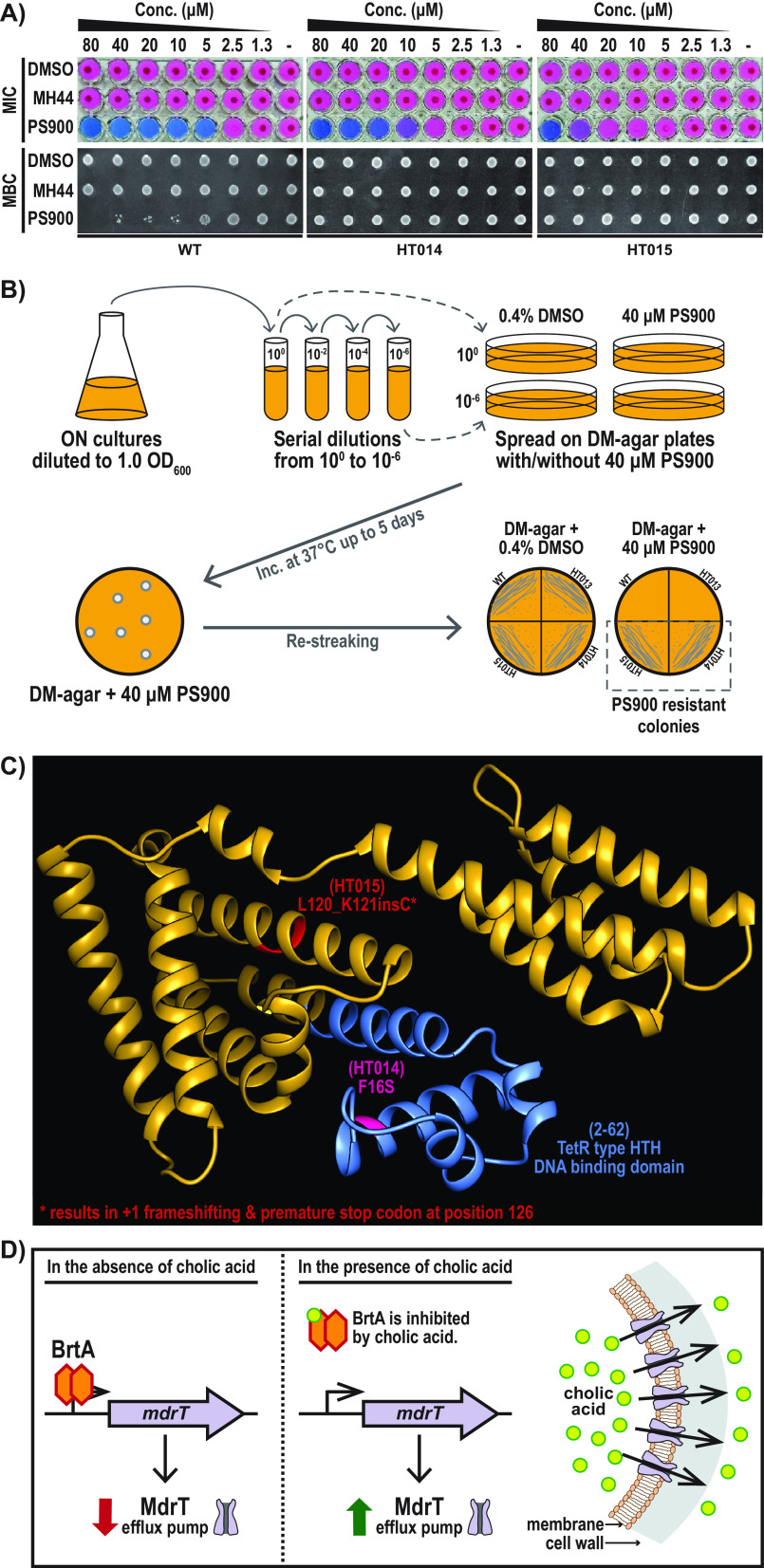
FIG 2.
PS900 inhibits L. monocytogenes growth in defined medium. (A) Representative images showing the effect of PS900 on bacterial growth (MIC), scored by pellet formation and resazurin (blue)-to-resorufin (pink) conversion (see Materials and Methods). Bacterial survival (MBC, minimal bactericidal concentration) was scored by growth on BHI agar plates. The WT strain and PS900-resistant mutants (HT014 and HT015) were incubated overnight in defined medium with various concentrations of DMSO (control), MH44, or PS900 at 37°C (showing MICs). These samples were then spotted onto regular BHI agar plates, followed by 24 h of incubation at 37°C (showing MBCs). The images are representative of three individual experiments. (B) Schematic model depicting the PS900-resistant-mutant selection process. ON, overnight. (C) Predicted TetR-type HTH DNA binding domain (blue) and the amino acid substitutions found in the BrtA protein in the HT014 (pink) and HT015 (red) strains are highlighted on the AlphaFold-predicted structure of the BrtA protein (Fig. S3) (52, 53). (D) Schematic model depicting the regulation of MdrT efflux pump expression by transcriptional repressor BrtA in the absence or presence of cholic acid (16).