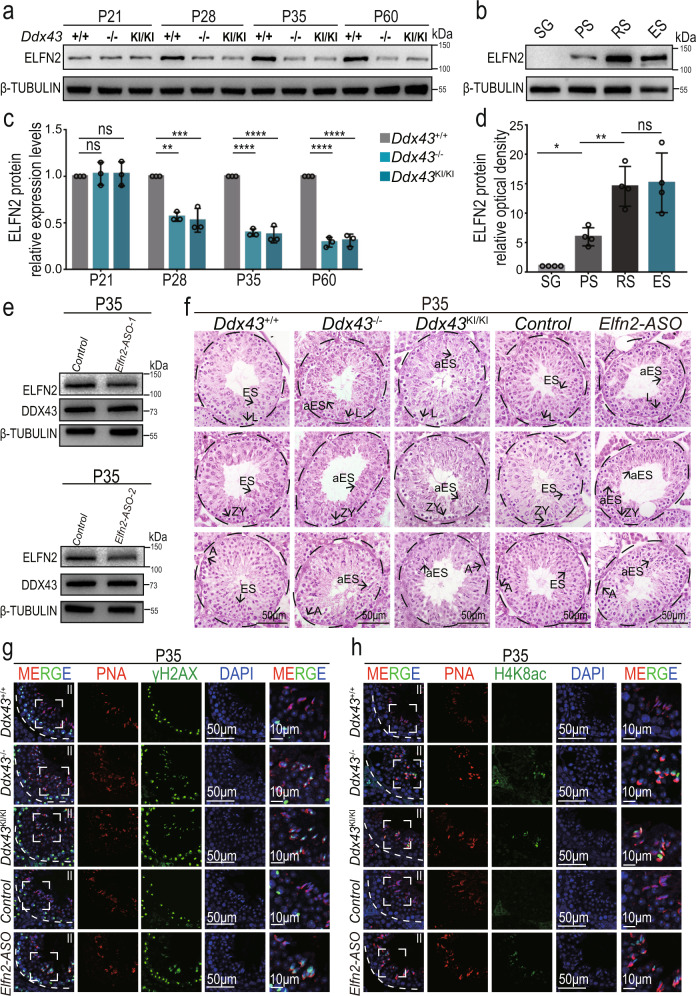
Fig. 7. Elfn2 knockdown in mouse testis reproduces similar spermatid defects in Ddx43 mutants.
a, b Western blot analyses of ELFN2 protein in extracts from wild-type and two Ddx43 mutant testes at indicated postnatal time points (a) and spermatogenic cells purified from wild-type mice (b), including spermatogonia (SG), pachytene spermatocytes (PS), round spermatids (RS), and elongating spermatids (ES). β-TUBULIN serves as a loading control. c, d Quantification of the ELFN2 protein levels in (a) and (b). The expression levels of ELFN2 are normalized to β-TUBULIN. The relative ELFN2 expression levels in Ddx43+/+ testes (a) and SG (b) are set at 1.0. P values were calculated by oneway ANOVA. ns, not significant; P = 0.9438 (Ddx43+/+ vs Ddx43–/– at P21), P = 0.9474 (Ddx43+/+ vs Ddx43KI/KI at P21), **P = 0.0013 (Ddx43+/+ vs Ddx43–/– at P28), ***P = 0.0008 (Ddx43+/+ vs Ddx43KI/KI at P28), **** P < 0.0001, *P = 0.0226 (SG vs PS), ** P = 0.008 (PS vs RS), P = 0.8982 (RS vs ES). Data presented are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. e Western blot analyses confirmed that ELFN2 protein was efficiently knocked down in Elfn2 knockdown mouse lysates. β-TUBULIN serves as a loading control. f H&E staining analyses using P35 testis sections prepared from Ddx43+/+, Ddx43KI/KI, Ddx43–/–, Elfn2 control and ASO-transduced P35 testes. Scale bars are indicated. A, type A spermatogonia; L, leptotene spermatocyte; ZY, zygotene spermatocyte; ES, elongating spermatid; aES, abnormal elongating spermatid. Results shown are representative of a minimum of three animal samples used for each genotype. g, h Immunofluorescence analyses using P35 testis sections of indicated genotypes with two combinations: γH2AX (green) and PNA (red) (g); H4K8ac (green) and PNA (red) (h). The rightmost panels show magnified images of the boxed area in the left panels. DNA was counterstained with DAPI. Stage numbers and scale bars are indicated. Each experiment was repeated three times with similar results.