Figure 1.
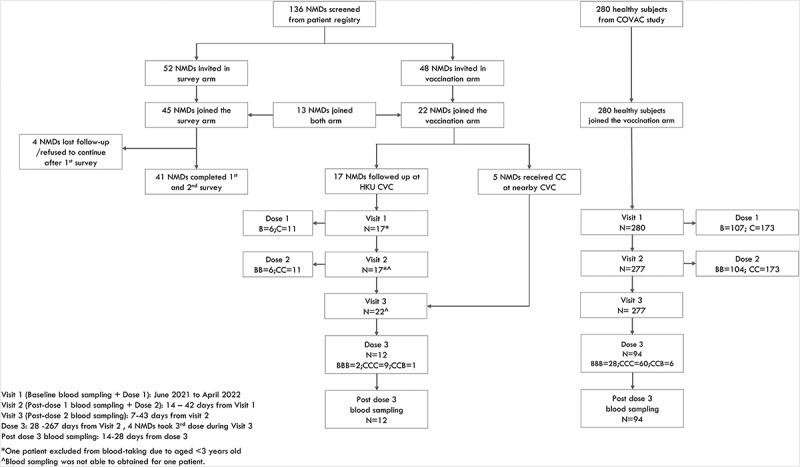
Flow diagram of study participants.
One hundred and thirty-six patients with neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) were screened from the patient registry. Fifty-two patients were invited to complete the hesitancy survey arm, and 48 patients were invited to join the reactogenicity and immunogenicity arm of the study. Forty-five patients completed the first hesitancy survey, and 41 (91.1%) of them completed both first and second surveys. For the reactogenicity and immunogenicity arm of the study, 22 patients joined and 17 were inoculated with BNT162b2 or CoronaVac at our University of Hong Kong (HKU) Community Vaccination Centers (CVCs) research site. These patients recorded adverse reactions in a 7-day diary system after vaccination for reactogenicity/safety analyses and had blood sampling. Additionally, five patients who received two doses of CoronaVac at nearby CVCs and had blood sampling after the second dose. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity data from healthy children and adolescents (n = 280) used for comparisons with patients with NMDs were retrieved from our previous publication.27 CVCs = Community Vaccination Centers research site, NMDs = patients with neuromuscular diseases, COVAC = Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) Vaccination in Adolescents and Children, HKU = University of Hong Kong. B, 1 dose of BNT162b2; BB, 2 doses of BNT162b2; C, 1 dose of CoronaVac; CC, 2 doses of CoronaVac; BBB, 3 dose of BNT162b2; CCC, 3 doses of CoronaVac; CCB, 2 doses of CoronaVac and 1 dose of BNT162b2.
