Figure 6. Human disease-associated mutations hyperactivate bacterial NACHT proteins.
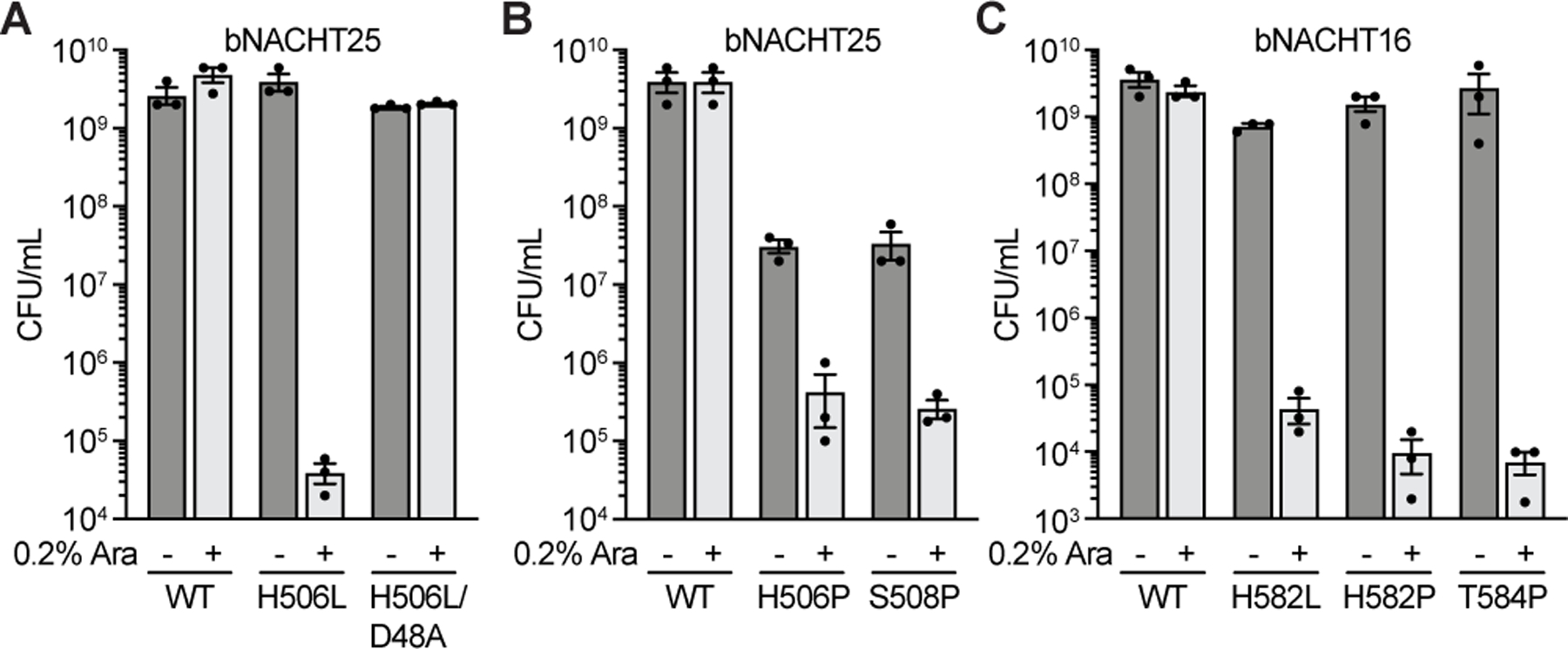
(A)–(B) Quantification of colony formation of E. coli expressing wild-type (WT) bNACHT25 or alleles with the indicated mutations.
(C) Quantification of colony formation of E. coli expressing bNACHT16 with the indicated mutations. See Figure S7 for an alignment of NLRC4, bNACHT16, and bNACHT25. For A–C, gene expression was induced with arabinose. Symbols denote induction (+) or lack of induction (−). Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 biological replicates, shown as individual points.
