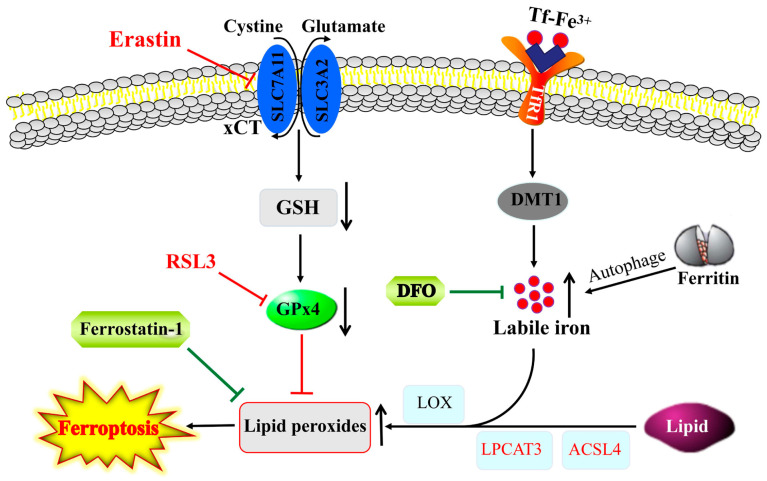
Figure 2.
Interplay between ferroptosis and iron homeostasis. Lipid peroxides that induce ferroptosis are produced through auto-oxidation and/or enzymatic activity of LOX on lipid esters generated from lipids via the activity of ACSL4 and lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3). GPx4 blocks ferroptosis by converting lipid peroxides to lipid alcohols, whereas reductions in GSH or GPx4 activity by blocking of xCT antiporter (e.g., by erastin) or inhibiting of GPx4 (e.g., RSL3) can trigger ferroptosis. The increase in labile iron pool in the cytosol via an increased iron uptake through TfR1 and/or autophagic degradation of ferritin can exacerbate ferroptosis via facilitating lipid peroxidation, and, thus, iron chelators, such as DFO and ROS scavengers (e.g., ferrostatin-1), suppress ferroptosis.