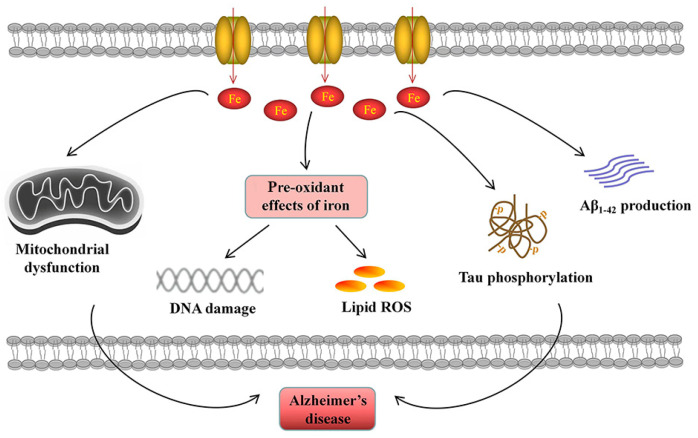
Figure 5.
Iron accumulation participates in the pathogenesis of AD. Elevated cellular iron is related to Aβ1-42 production and tau phosphorylation. Excessive iron leads to mitochondrial dysfunction. The pre-oxidant effects of iron induce DNA damage and lipid ROS generation, contributing to cell death.