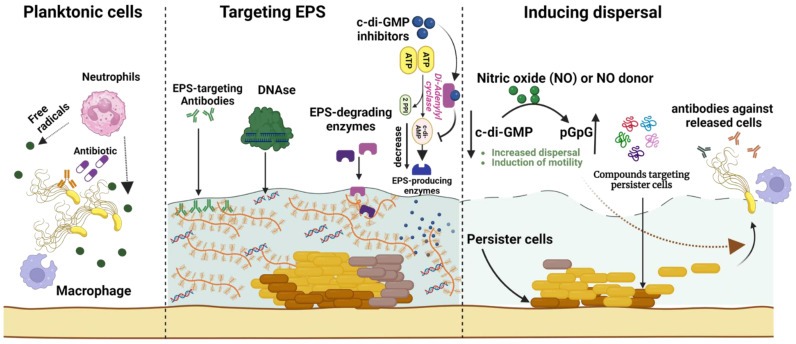
Figure 4.
A comprehensive overview of biofilm eradication strategies for overcoming infection scenarios. These strategies include targeting biofilm extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) via degradation enzymes (e.g., DNases or glucanohydrolases), EPS-specific antibodies, and cyclic-di-guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) inhibitors that subsequently reduce EPS production. Additional approaches facilitate biofilm dispersal by employing nitric oxide to activate proteins that hydrolyze c-di-GMP, thereby boosting biofilm cell dispersal and motility. These dispersed cells become susceptible to destruction by innate immune cells (such as macrophages and neutrophils) via phagocytosis and free radical release, or due to antibiotic treatment. The diagram also depicts antibiofilm agents (e.g., small peptides) that specifically target persister cells within the biofilm core to eradicate recurring biofilm-associated infections. The figure was created using biorender.com, accessed on 28 May 2023.