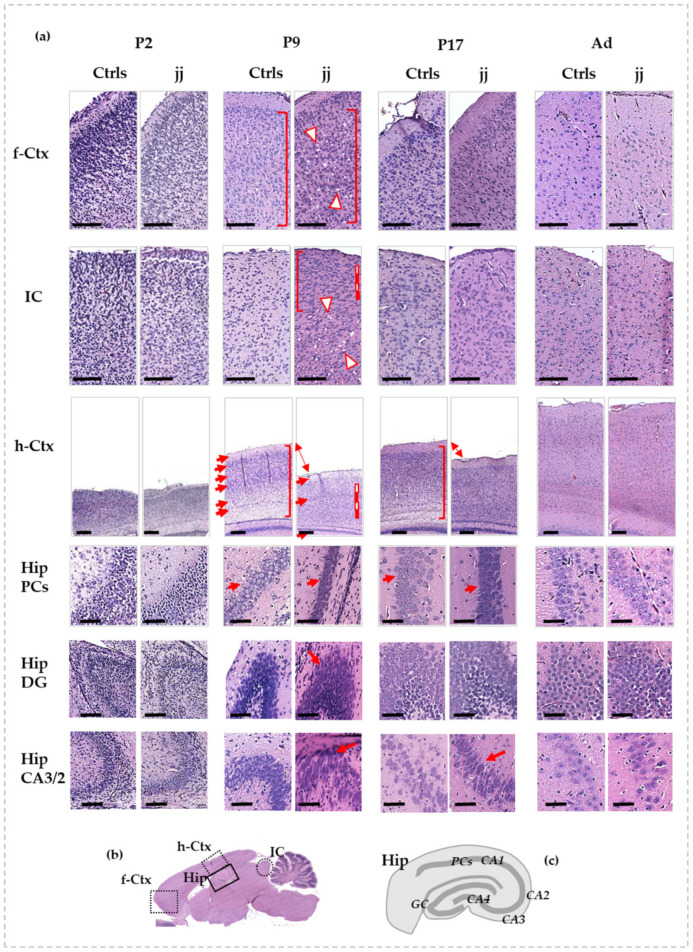
Figure 1.
Histological features of f-Ctx, h-Ctx, IC, and Hip of developing Gunn rats compared to age-matched controls. In (a): Histologic pictures showing the major alterations observed in jj vs. Ctrls rats. P—postnatal age in days; Ad—adults, more than 6-month-old; jj—hyperbilirubinemic Gunn rats; Ctrls—normobilirubinemic age-matched Gunn rats; f-Ctx—frontal cortex; h-Ctx—parietal cortex; IC—Inferior colliculi; Hip—hippocampus; PCs—pyramidal cells; DG—Dentate gyrus; CA—Cornus of Ammonis. Red-white triangles: necrotic lesions. Red and white lines: attracting attention to cellular density. Red square bracket: attracting attention to cellular heterogeneity. Red arrows: drawing attention to different tissue organization, layers, architecture, and shapes of cells. Double arrow: attracting attention to the different thickness. Scale bar: 100 um in each figure. (b) A picture showing where each region under study is located on the rat brain. (c) A representative picture of the Hip structure.