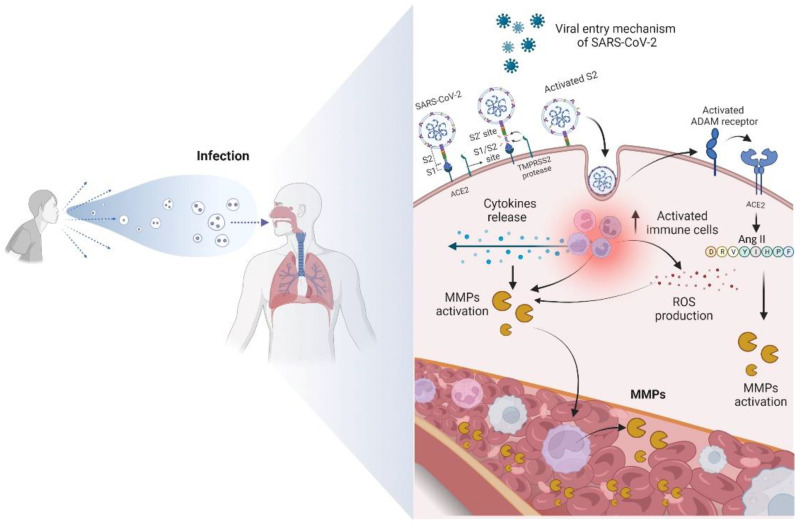
Figure 2.
Overview of the main mechanism of entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cell and the biomolecular changes that occur from contamination. The virus binds to the ACE2 receptor, becoming active. The contact of SARS-CoV-2 with the cell membrane then enables the activation of ADAM receptors, favoring the increase in ANG II and expression of MMPs. The activation of immune cells produces ROS and a cytokine storm, promoting the proteolytic activation of MMPs and consequent increase in the levels of these enzymes in the bloodstream.