Table 1.
Main tools commonly used in the assessment of HS severity and disease burden.
| Clinical and Research Settings | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) | |||
IHS4 (point) =
| |||
| |||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
| Hurley Staging System | |||
| Stage | I | II | III |
| Abscess | Single or multiple | Single or multiple, widely separated, recurrent | Diffuse or near-diffuse involvement |
| Sinus tract | – | + | Multiple interconnected |
| Cicatrization | – | + | + |
| Area | Entire area | ||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
| Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response—HiSCR | |||
HiSCR is defined by the status of three types of criteria lesions, considering abscesses (fluctuant, with or without drainage, tender or painful), inflammatory nodules (tender, erythematous, pyogenic granuloma lesion), and draining fistulas (sinus tracts, with communications to skin surface, draining purulent fluid). The proposed definition of responders to treatment (HiSCR achievers) is:
| |||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
| Hidradenitis Suppurativa Physician’s Global Assessment (HS-PGA) | |||
| HS-PGA | |||
| Clear (score = 0) | 0 abscesses, 0 draining fistulas, 0 inflammatory nodules, and 0 non-inflammatory nodules | ||
| Minimal (score = 1) | 0 abscesses, 0 draining fistulas, 0 inflammatory nodules, and presence of non-inflammatory nodules | ||
| Mild (score = 2) | 0 abscesses, 0 draining fistulas, and 1–4 inflammatory nodules; or 1 abscess or draining fistula and 0 inflammatory nodules | ||
| Moderate (score = 3) | 0 abscesses, 0 draining fistulas, and 1 ≥ 5 inflammatory nodules; or 1 abscess or draining fistula and ≥1 inflammatory nodule; or 2–5 abscesses or draining fistulas and <10 inflammatory nodules | ||
| Severe (score = 4) | 2–5 abscesses or draining fistulas, and ≥10 inflammatory nodules; | ||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
| Patient-Reported Outcomes | |||
| Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI Score) | |||
| DLQI Total score | |||
| 0–1 | No effect on patient’s life | ||
| 2–5 | Small effect on patient’s life | ||
| 6–10 | Moderate effect on patient’s life | ||
| 11–20 | Very large effect on patient’s life | ||
| 21–30 | Extremely large effect on patient’s life | ||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
| Pain Visual Analog Scale (Pain VAS) and Numeric Rating Scale (NRAS) for Pain | |||
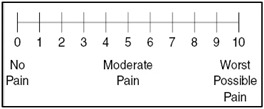
| The pain VAS is a continuous scale comprised of a horizontal (HVAS) or vertical (VVAS) line, usually 10 cm in length, anchored by 2 verbal descriptors, one for each symptom extreme. The NRAS for pain is a single 11-point numeric scale, which can be administered verbally or graphically. Response options/scale. For pain intensity, both scales are most commonly anchored by “no pain” (score of 0) and “pain as bad as it could be” or “worst imaginable pain” (score of 10). | |||

|
|
||
| Advantages | Limitation | ||
|
|
||
