Table 1.
A comparison table of the devices under review by category. The black arrows indicate the direction of the electric field for each electroceutical. Dressings are universally represented by a cream-colored substrate; silver, copper, and zinc are represented as their elemental colors; wound fluid is depicted as blue; and harmful bacteria are green.
| Ionic | Wireless | Battery-Powered | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The electrochemical gradient drives ions to the bacterial cell. Where the local electrochemical gradient is high enough, ions are driven into the cell where they disrupt the respiratory system and bind to DNA. | The electrochemical potential difference creates an electric field that is maintained by ion transport between the anode and cathode until the electrochemical reaction reaches equilibrium. | An electric potential is applied to an inert electrode and the field is maintained until the battery depletes. | |||
| Commercial name | Reference(s) | Commercial name | Reference(s) | Commercial name | Reference(s) |
| Silver sulfadiazine | [43,44] | Procellera | [45,46] | Patterned electroceutical dressing |
[42] |
| Acticoat | [47,48] | ||||
| Actisorb | [49] | PosiFectRD | [6,19,50,51,52] | ||
| Aqucel-Ag | [53,54,55] | ||||
| Contreet Foam | [43,44,53,56,57] | Yu et al. | [58] | Accel-Heal | [59,60,61] |
| Urgotul | [43,44,53,56,57] | ||||
| MedCu | [62,63] | WoundEL | [60,64] | ||
| Metcovazin | [24,65,66,67,68] | ||||
| Mode of action | Mode of action | Mode of action | |||
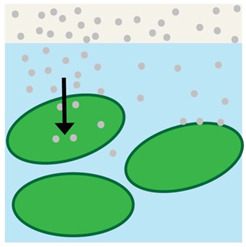 Silver circles represent silver ions, green ovals represent bacteria, and black arrows represent the electrochemical gradient. |
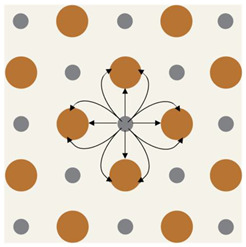 Silver circles represent silver electrodes, copper circles represent copper electrodes, and black arrows represent the electrochemical gradient. |
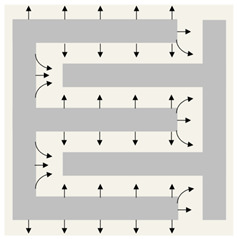 Silver rectangles represent silver electrodes, beige represents the inert dressing, and black arrows represent the electrochemical gradient. |
|||
