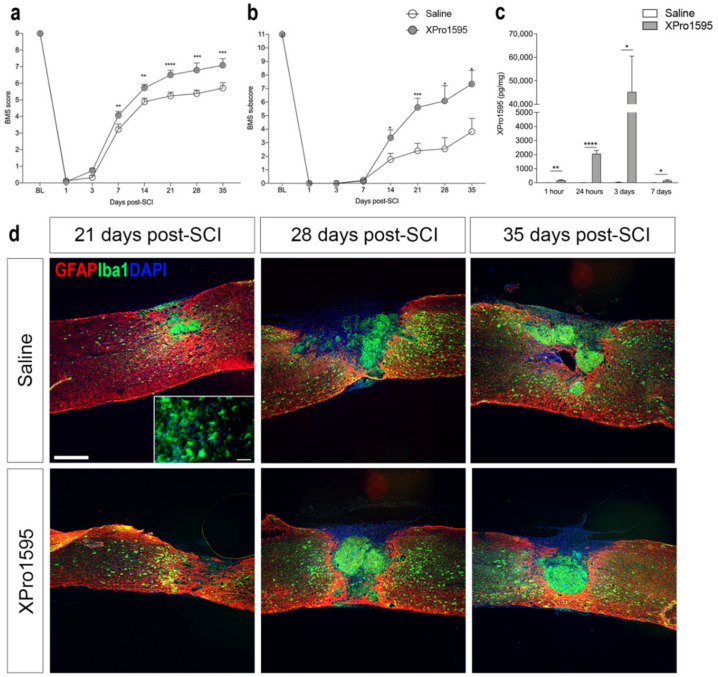
Figure 1.
Topical inhibition of solTNF improves functional outcomes after SCI. (a) Evaluation of hindlimb locomotor function. XPro1595- and saline-treated mice were tested 1 and 3 days after SCI and weekly thereafter for 5 weeks. Motor behavior was scored under blinded conditions with the BMS (n(day 1–21) = 25 mice/treatment group and n(day 28–35) = 11–12 mice/treatment group). Two-way ANOVA (Time: F3.76,152.7 = 724.4, p < 0.0001, Treatment: F1,48 = 13.41, p = 0.0006, Interaction: F7,284 = 5.07, p < 0.0001) followed by Fisher’s LSD test: t(day 1)332 = 0.21, p = 0.36; t(day 3)332 = 1.50, p = 0.14; t(day 7)332 = 2.99, p = 0.003; t(day 14)332 = 2.99, p = 0.002; t(day 21)332 = 4.49, p = 0.00001; t(day 28)332 = 3.50, p = 0.0005; and t(day 35)332 = 3.40, p = 0.0008. (b) Evaluation of BMS subscores (n(day 1–21) = 25 mice/treatment group and n(day 28–35) = 11–12 mice/treatment group). Two-way ANOVA (Time: F7,270 = 122.8, p < 0.0001, Treatment: F1,270 = 32.53, p < 0.0001, Interaction: F7,270 = 5.26, p < 0.0001) followed by Fisher’s LSD test: t(day 1)332 = 0.21, p = 0.36; t(day 3)332 = 1.50, p = 0.14; t(day 7)48 = 0.44, p = 0.66; t(day 14)48 = 3.62, p = 0.04; t(day 21)48 = 3.62, p = 0.0007; t(day 28)21 = 2.50, p = 0.02; and t(day 35)21 = 2.49. p = 0.02. (c) XPro1595 levels 1 h as well as 1, 3, and 7 days after SCI measured by electrochemiluminescence in saline- and XPro1595-treated mice (n = 4–5 mice/treatment group). (d) Sections of spinal cords from saline- and XPro1595-treated mice with 21, 28, or 35 days survival after SCI double labeled for astroglial GFAP (red) and microglial/macrophage Iba1 (green). 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) was used as a nuclear marker. Scale bar = 200 μm. Insert: Iba1+ ramified microglia located in the peri-lesion area of a saline-treated mouse 21 days after SCI. Scale bar = 40 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Iba1, ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; SCI, spinal cord injury.