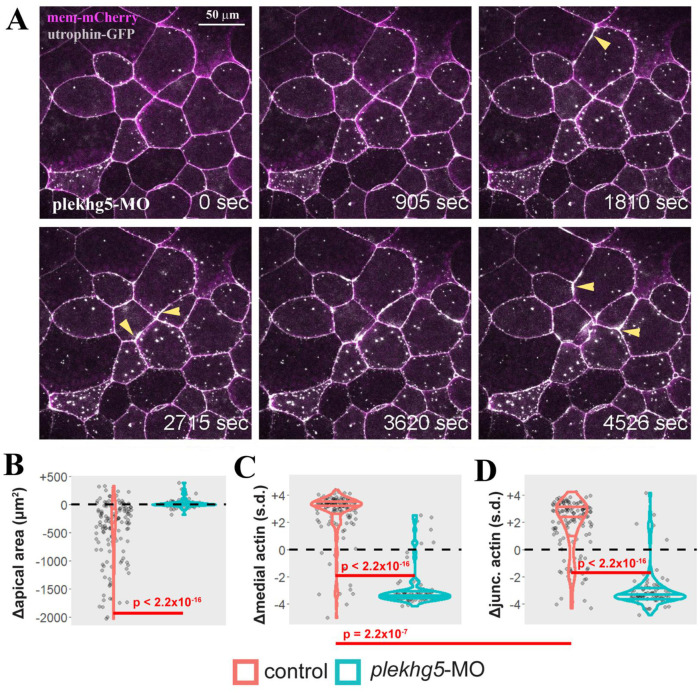
FIGURE 4:
Knockdown of plekhg5 prevents apical accumulation of F-actin and reduction of apical cell size. (A) Selected frames from a time-lapse movie show that despite the initial F-actin dynamics and formation of F-actin puncta, the cells with plekhg5 knockdown fail to increase apical F-actin signal or reduce the apical surface. Instead, junctional F-actin flares can be seen frequently. The arrowheads point to examples of F-actin flares. (B) Quantification of apical cell area demonstrates that unlike cells in control embryos (Supplemental Movies 1 and 2), cells from plekhg5 knockdown embryos (Supplemental Movies 3 and 4) cannot reduce their apex efficiently. (C, D) While medial and junctional F-actin intensity increases during apical constriction of bottle cells in control embryos, the intensity of medial and junctional F-actin decreases in cells from plekhg5 knockdown embryos. Each dot is an individual cell. Horizontal lines within each violin delineate quartiles along each distribution. s.d. = standard deviations. P values were calculated via a KS test. Data were collected from four control and five plekhg5 knockdown embryos.